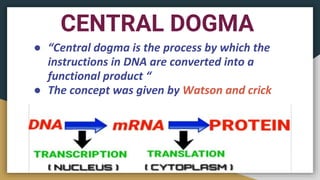
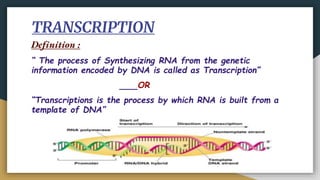
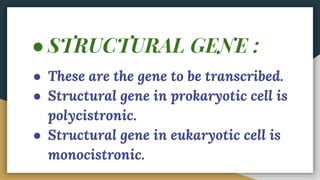
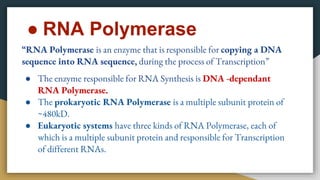
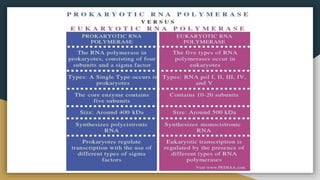
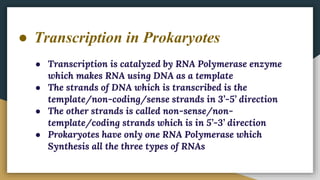
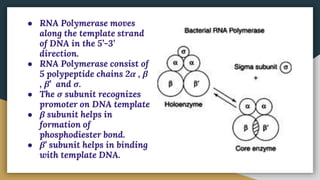
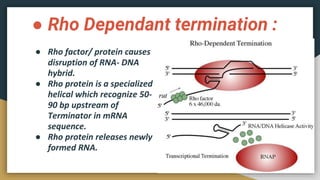
This document summarizes the process of transcription in bacteria. It defines transcription as the synthesis of RNA using a DNA template. There are three main classes of RNA - mRNA, rRNA and tRNA. Transcription requires a promoter, structural gene, terminator, RNA polymerase and other factors. RNA polymerase moves along DNA in the 5'-3' direction synthesizing RNA in the 3'-5' direction using complementary base pairing. Transcription includes initiation, elongation and termination steps. Termination can be rho-independent involving a hairpin loop or rho-dependent using a rho termination factor.