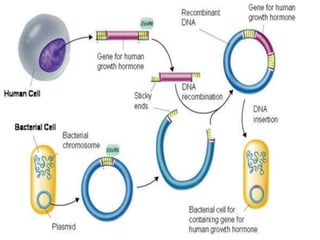
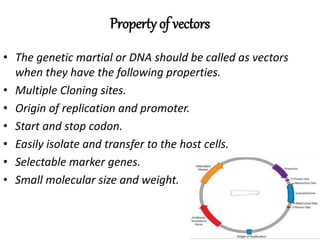
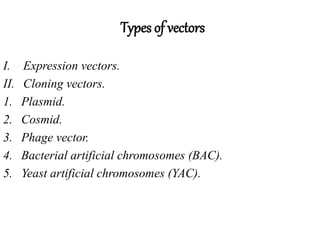
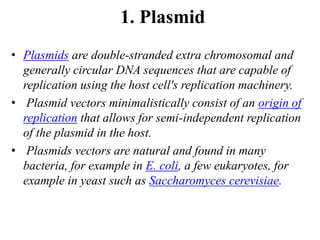
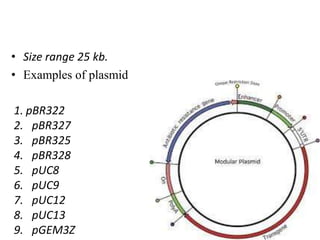
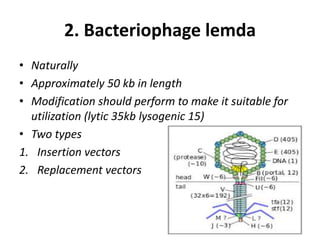
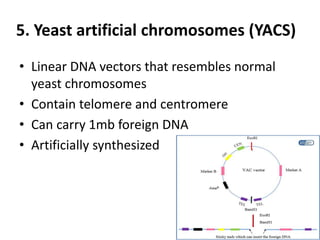
Vectors are DNA molecules that can carry foreign DNA into host cells. There are two main types of vectors - expression vectors, which are used to produce proteins, and cloning vectors, which are used to replicate and clone DNA fragments. Common cloning vectors include plasmids, cosmids, phage vectors like lambda, and bacterial and yeast artificial chromosomes. Plasmids are small, circular DNA molecules that are commonly used to clone DNA fragments up to 12kb in size. Cosmids and phage vectors like lambda can carry larger fragments up to 45kb and 20kb respectively. Bacterial and yeast artificial chromosomes can carry even larger fragments up to 100kb and 1mb respectively but are more difficult to work with. All vectors require key