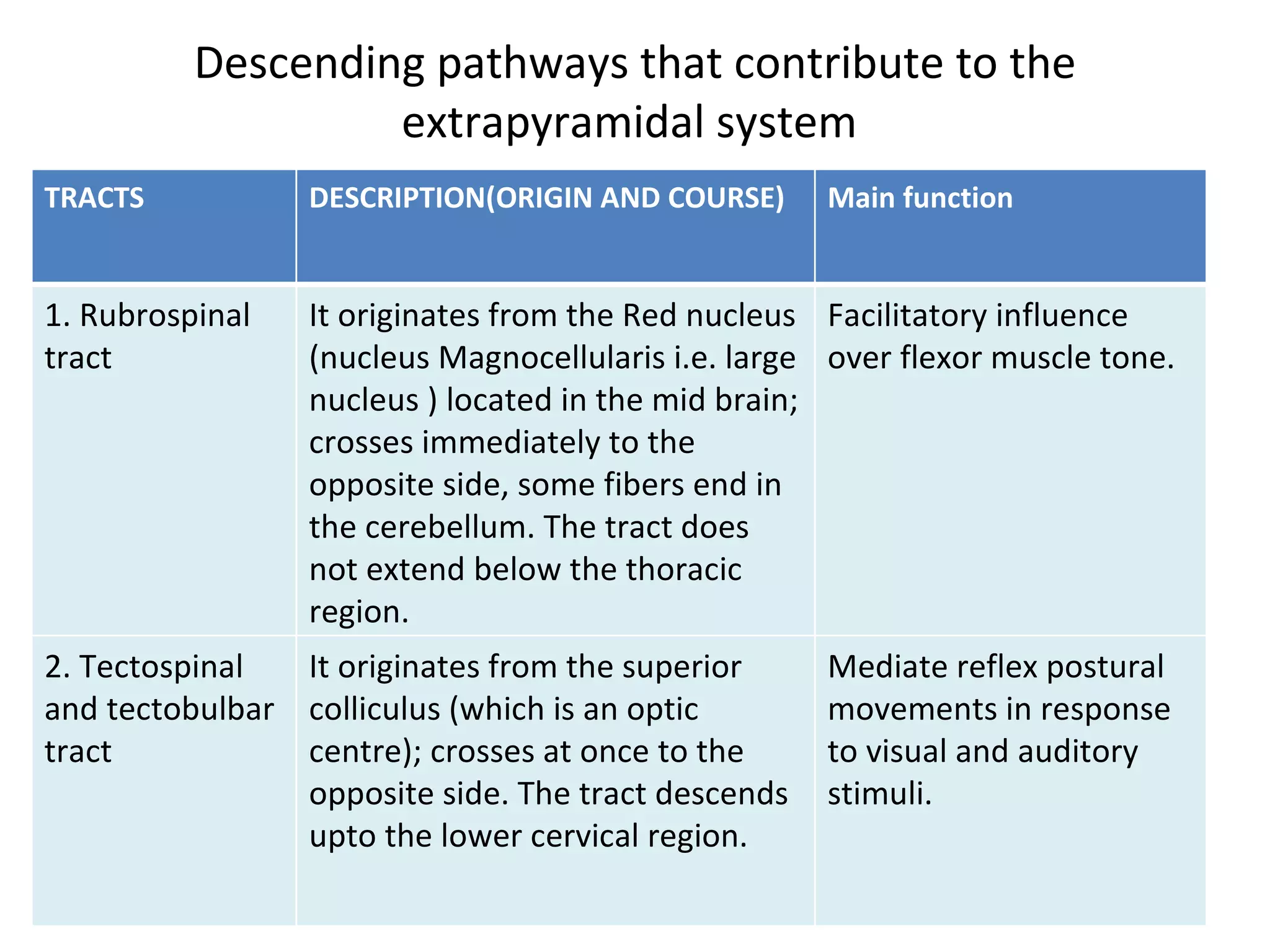
This document provides information about descending tracts in the central nervous system. It discusses the pyramidal tract and extrapyramidal tract, describing their origins, courses, terminations and functions. Specifically, it details the lateral and anterior corticospinal tracts of the pyramidal tract and their role in controlling voluntary movements. It also outlines several extrapyramidal tracts including the rubrospinal, tectospinal, reticulospinal and vestibulospinal tracts and their functions in tasks like muscle tone and posture. The document concludes by comparing the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts and differences between upper and lower motor neuron lesions.