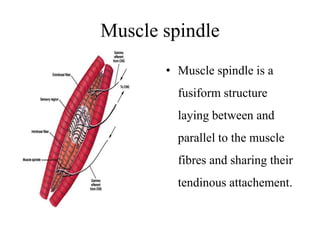
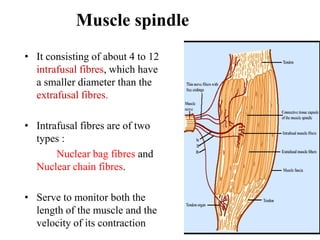
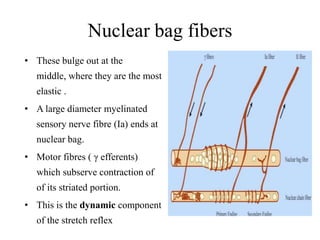
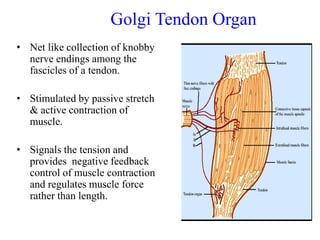
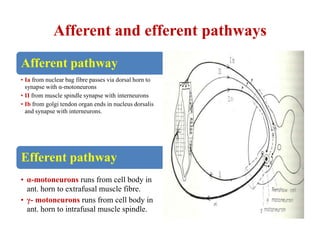
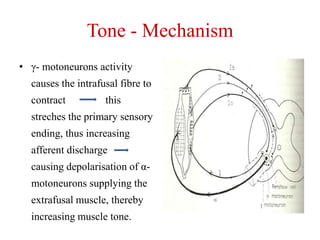
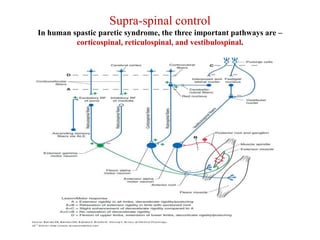
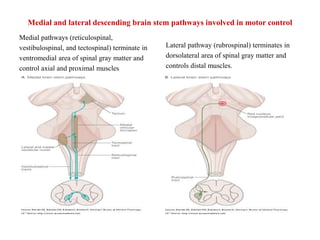
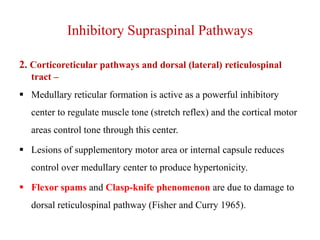
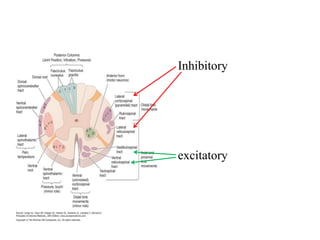
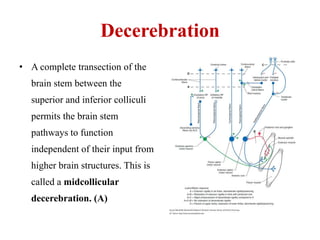
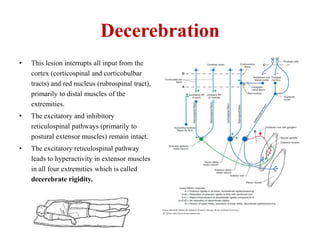
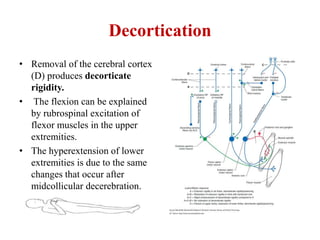
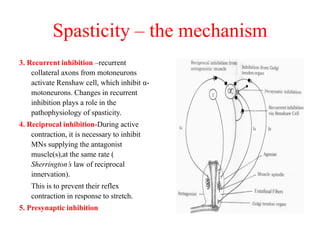
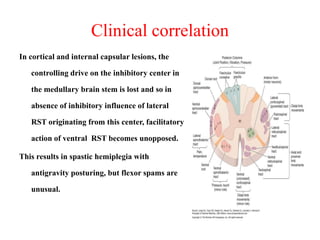
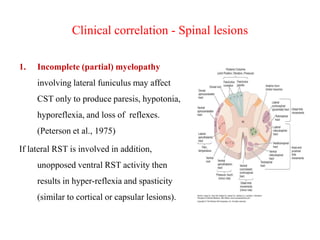
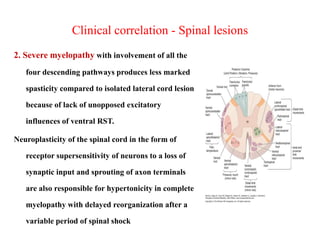
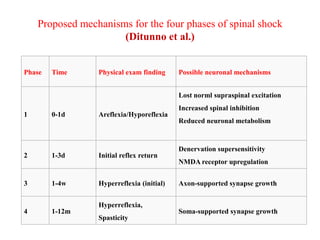
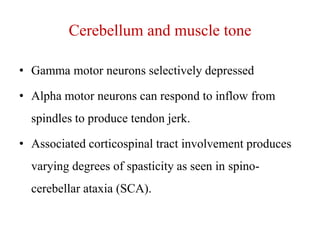
This document discusses muscle tone and its neurophysiology. It defines muscle tone as the resistance of a limb to passive movement. Muscle tone is controlled both by spinal and supra-spinal mechanisms. Spinally, the stretch reflex involving muscle spindles and alpha and gamma motoneurons controls tone. Supra-spinally, the reticulospinal and vestibulospinal tracts facilitate tone while the corticospinal tract inhibits it. Disorders of increased and decreased tone are also discussed, focusing on spasticity which results from loss of inhibition of spinal reflexes.