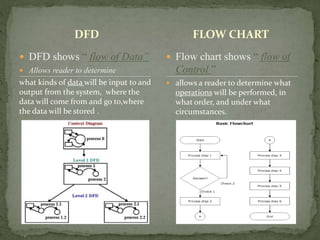
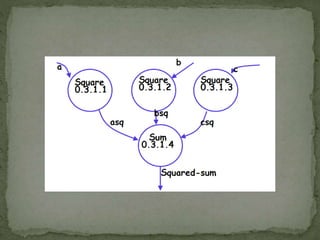
A data flow diagram (DFD) visually represents the flow of data within an information system, illustrating how data is transformed through various processes and where it is stored. It differentiates between external entities, processes, and data storage, allowing users to understand data inputs and outputs effectively. Context diagrams serve as the highest-level representation, while level 1 DFDs provide a more detailed breakdown of major processes.