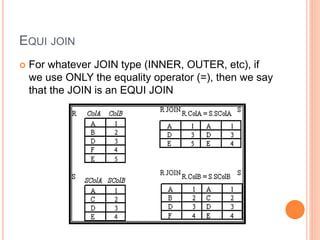
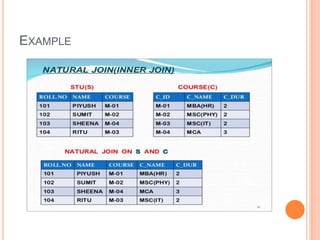
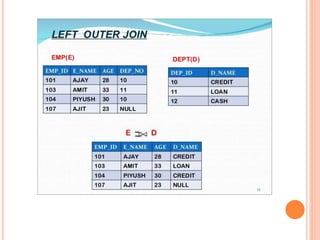
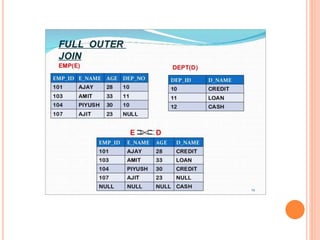
The document discusses database management systems, focusing on relational algebra and various join operations. It defines key operations such as selection, projection, and join, including types like theta join, equi join, natural join, and outer join. Each join type is explained with its characteristics and how it combines data from two relations.