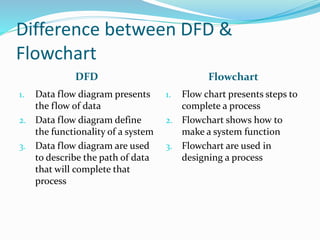
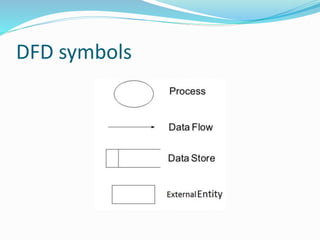
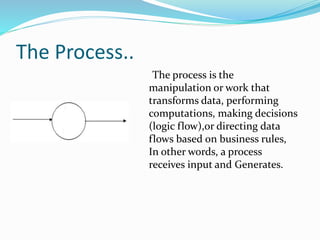
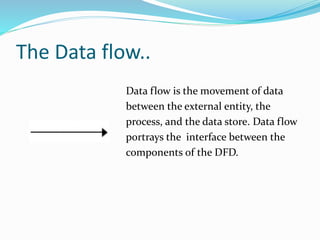
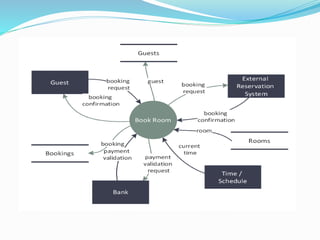
The document discusses Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs), including what they are, their history, types, symbols, and levels (level 0, 1, and 2 DFDs). DFDs graphically represent the flow of data through an information system and can be used to visualize data processing. They were originally proposed in the 1970s and differ from flowcharts in that they define system functionality and show data paths rather than process steps. DFDs help describe system boundaries, support data flow logic, and improve conceptual clarity for developers and clients.