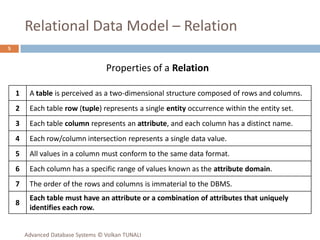
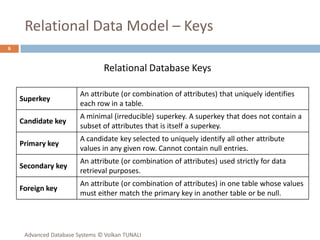
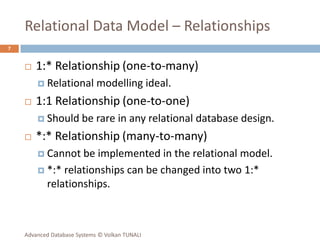
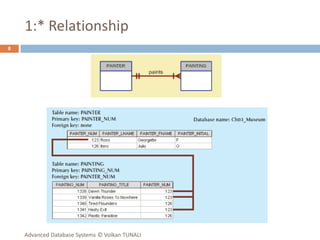
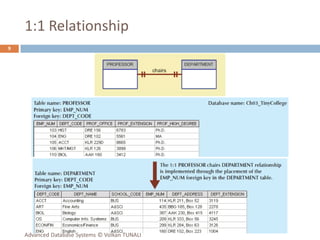
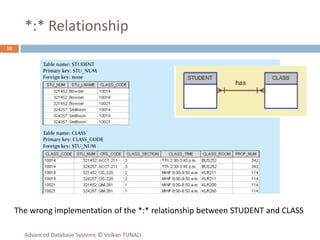
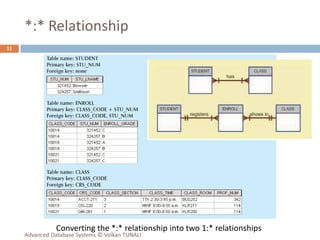
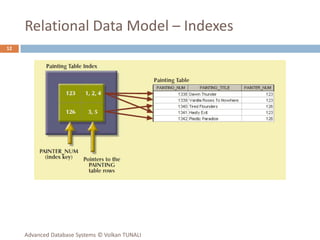
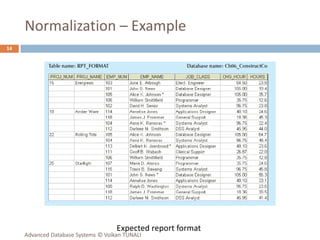
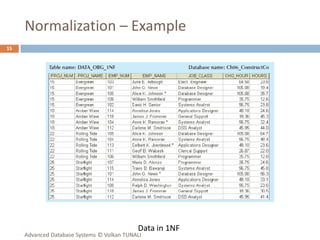
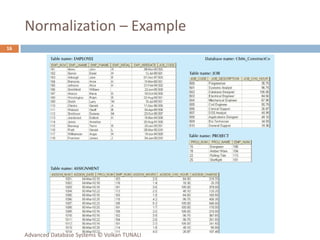
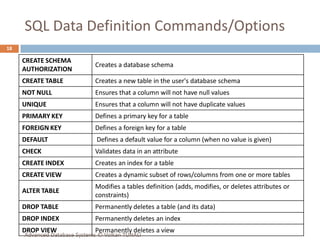
This document provides an overview of key database concepts including: the relational data model with tables, keys, relationships, and normalization; database management systems; SQL for defining, manipulating, and querying data; and advanced techniques like joins, set operations, and subqueries. It defines common data models, relational structures, and the SQL language for working with relational databases. Normalization is covered as a way to minimize redundancy and anomalies in tables.