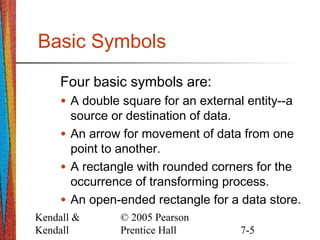
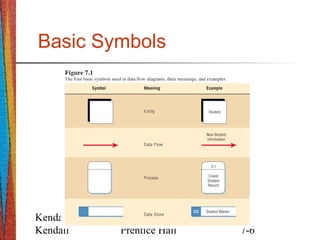
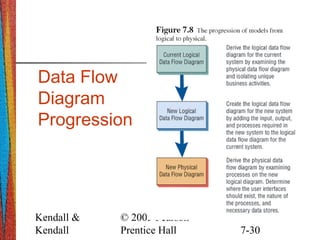
This document discusses data flow diagrams (DFDs), including their purpose, basic symbols, guidelines for creating them, and differences between logical and physical DFDs. DFDs graphically represent the flow of data through a process and emphasize the logic of a system. They are created at different levels, with the context-level diagram providing an overview and lower-level diagrams showing more detail on individual processes. Logical DFDs focus on business processes, while physical DFDs illustrate how a system will be implemented technically.