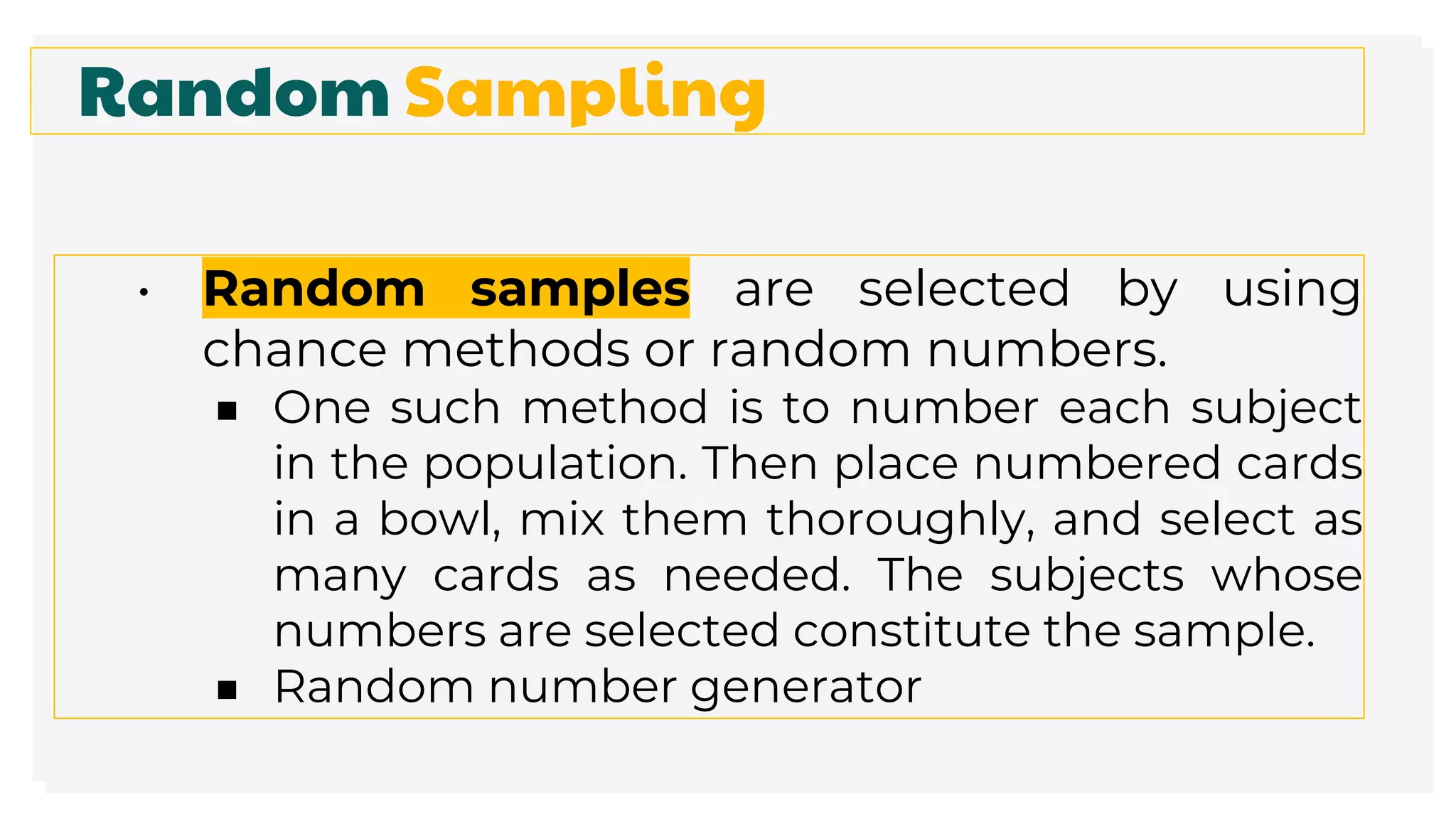
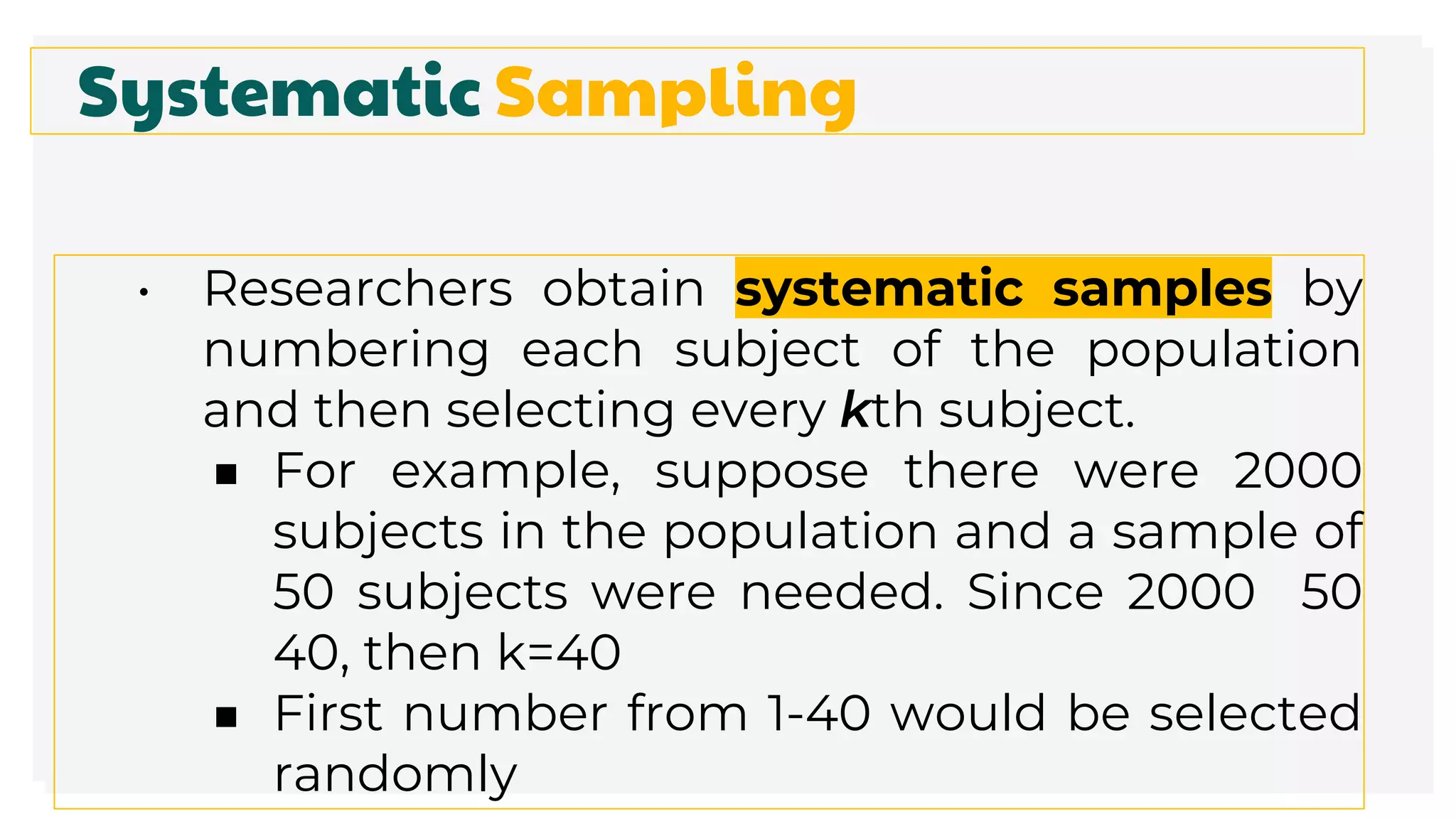
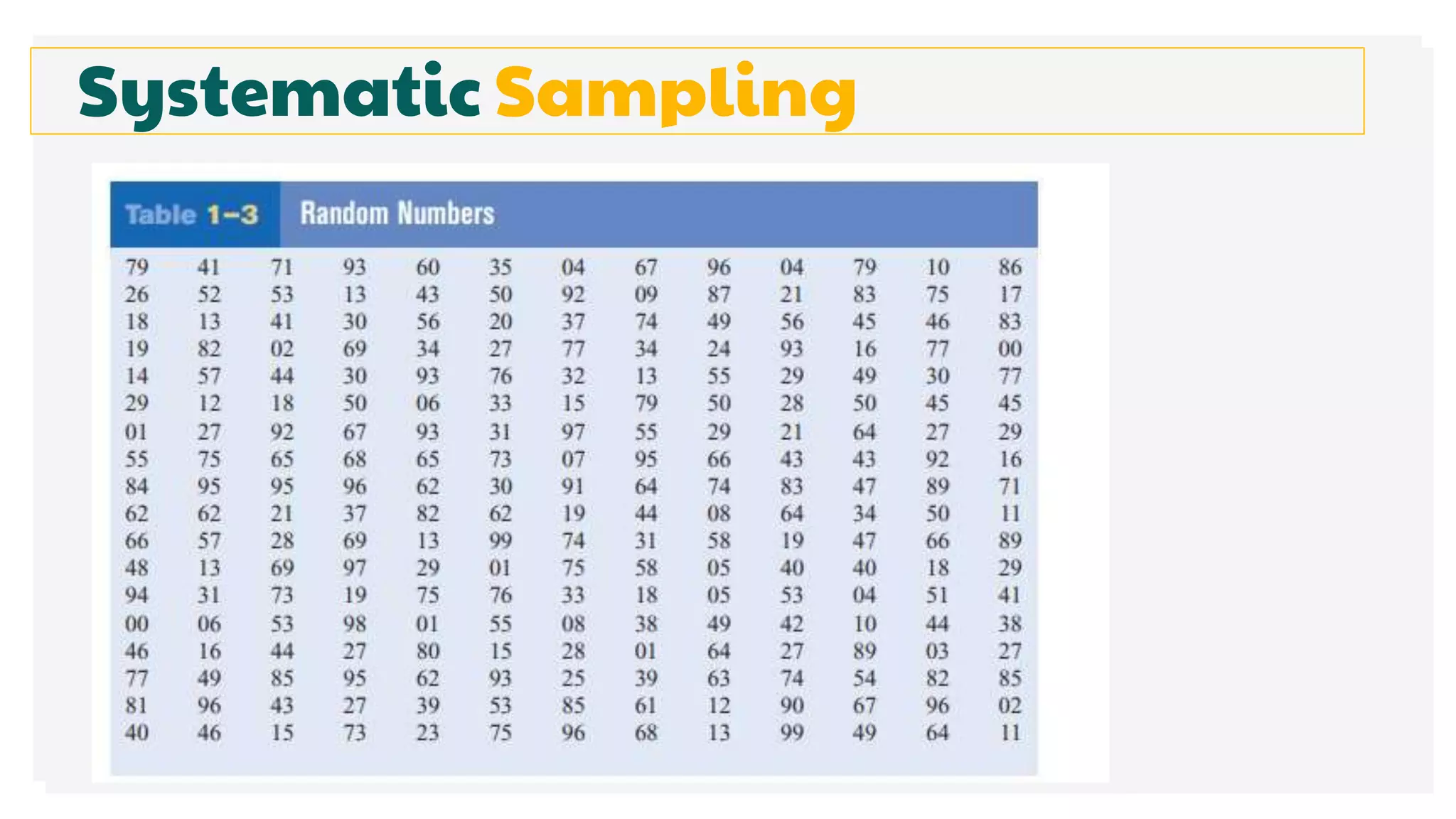
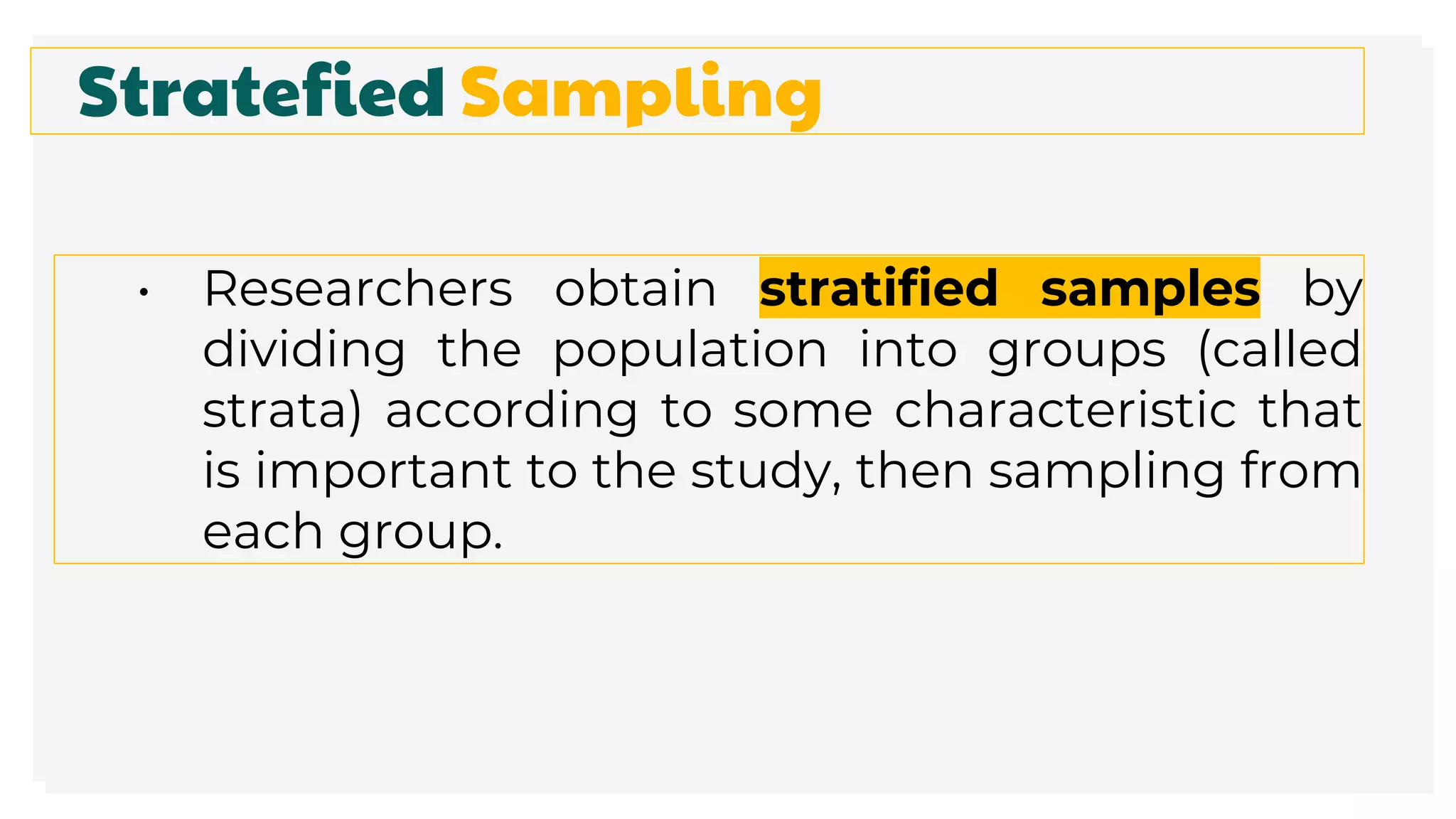
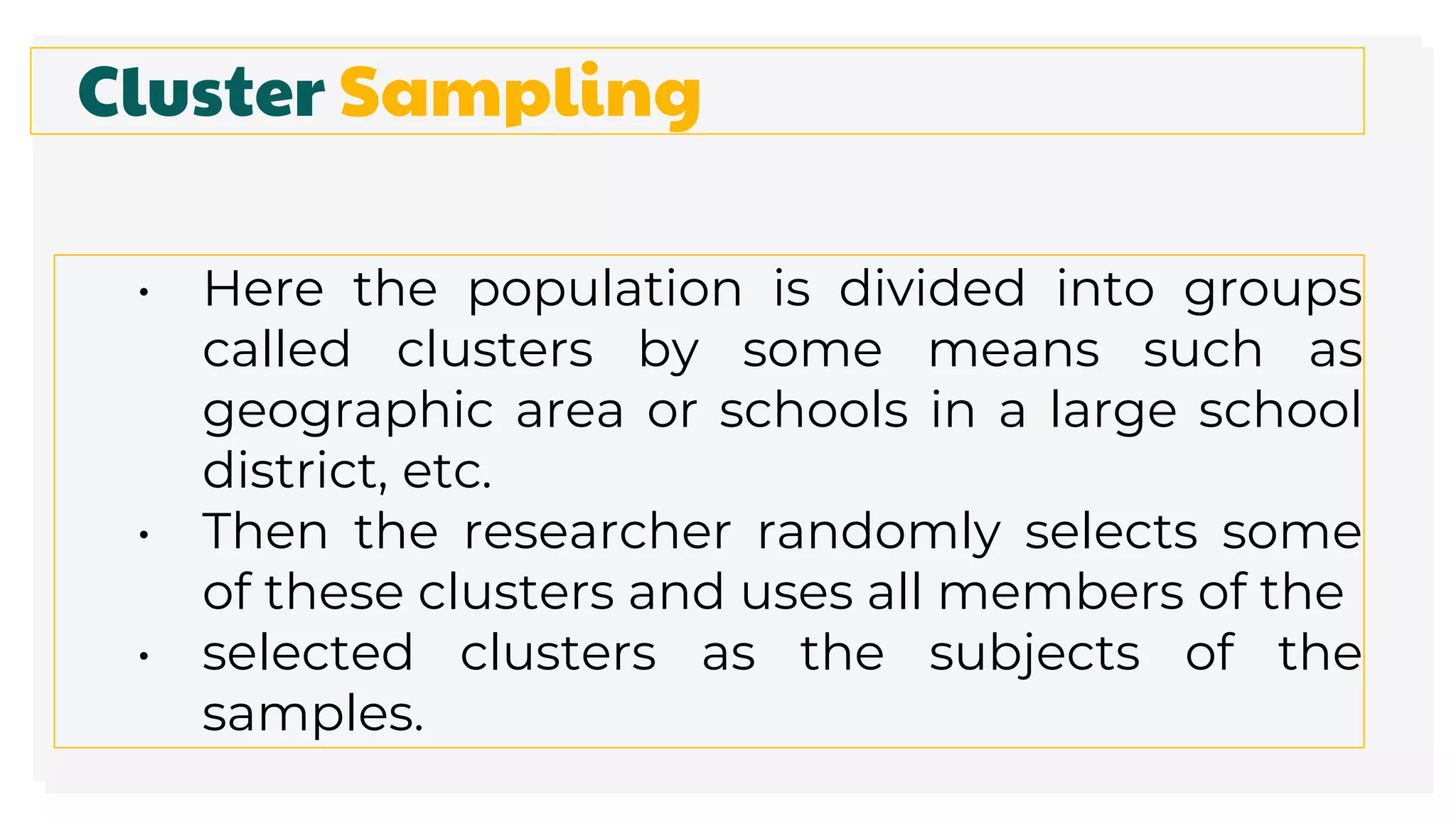
This document discusses different methods for collecting data and sampling techniques. It describes common data collection methods like surveys, questionnaires, and interviews. For sampling, it explains random sampling which uses chance to select subjects, systematic sampling which selects every kth subject, stratified sampling which divides a population into groups and samples from each, and cluster sampling which divides a population into clusters and randomly selects some clusters.