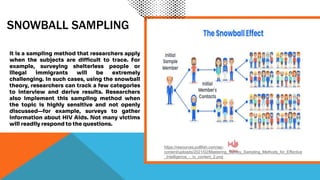
The document discusses various sampling methods used in research, defining key terms such as population, sample, and the process of sampling. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of sampling, as well as different techniques including probability sampling methods (e.g., simple random, stratified) and non-probability sampling methods (e.g., convenience, judgmental). The text is aimed at providing a comprehensive understanding of how to select appropriate samples to ensure accurate research outcomes.