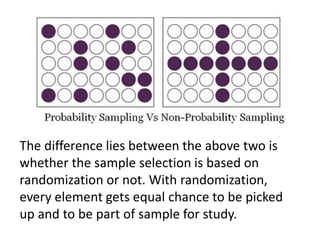
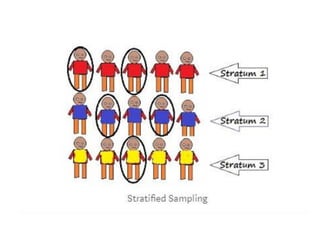
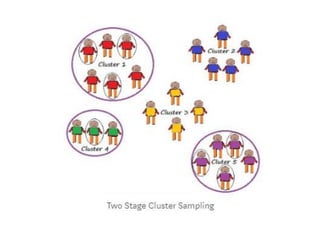
There are two main categories of sampling techniques: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. Probability sampling uses randomization to select samples so that every element has an equal chance of selection, ensuring representativeness. It includes simple random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, and systematic sampling. Non-probability sampling does not use randomization and can be biased; it includes convenience sampling, purposive sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. The sampling technique used determines how accurately the sample represents the population.