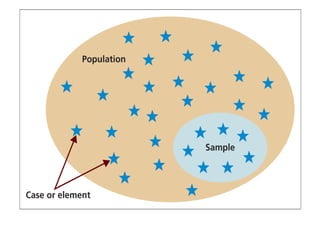
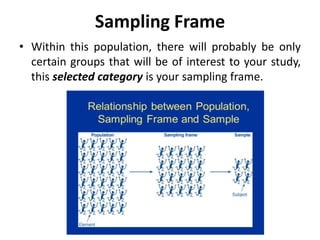
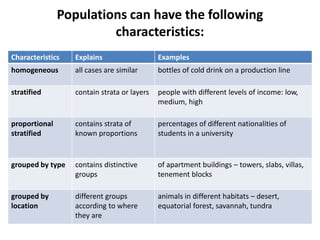
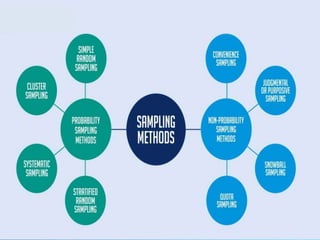
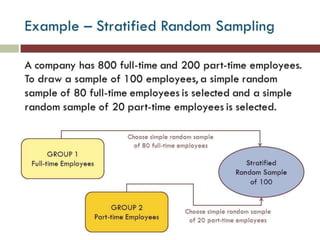
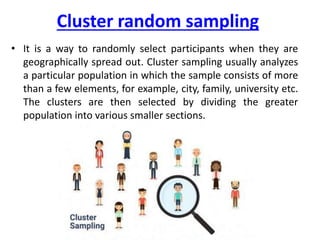
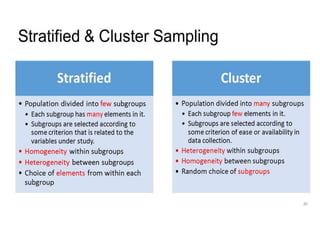
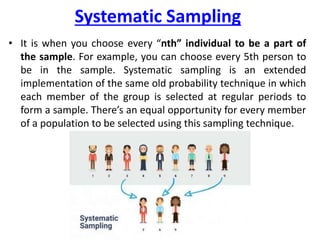
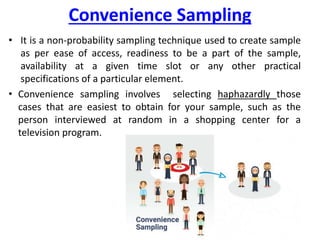
This document discusses sampling and various sampling methods. It defines sampling as selecting a small group from a larger population to make inferences about the whole population. There are two main types of sampling methods: probability and non-probability. Probability methods like simple random, stratified, cluster, and systematic sampling give reliable representations if done correctly. Non-probability methods like convenience, judgmental, snowball, and quota sampling rely on researcher judgment and cannot be generalized. The document provides details on each sampling technique.