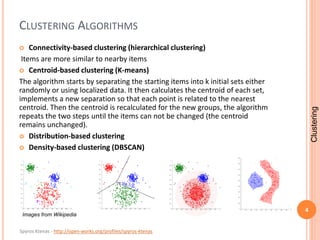
This document discusses data clustering techniques and algorithms. It describes clustering as the process of separating a set of objects into logical groups based on similarity. Common clustering applications include classification of species, customer segmentation, and grouping search engine results. Popular clustering algorithms mentioned include k-means, hierarchical, distribution-based, and density-based clustering. The document also summarizes several papers that propose optimizations to clustering algorithms like k-means in order to improve accuracy and efficiency. Finally, it notes initial progress on a PHP implementation of the k-means algorithm.