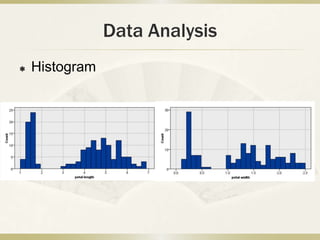
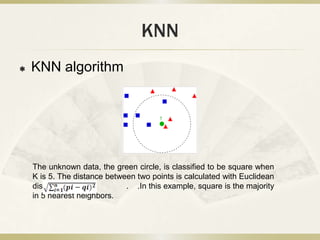
This document summarizes an analysis of the K-nearest neighbors (KNN) machine learning algorithm on the Iris dataset. KNN was implemented on the Iris dataset, which contains 150 records across 5 attributes for 3 types of iris flowers. Data processing involved organizing the data and analyzing statistics and histograms. KNN classification works by finding the K closest training examples in attribute space and voting on the label. Testing showed that KNN achieved high accuracy, especially with a balanced training set and K=7 neighbors. While simple, KNN performs well on datasets with continuous attributes like Iris.