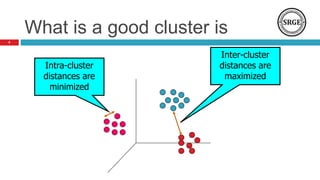
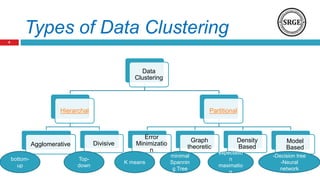
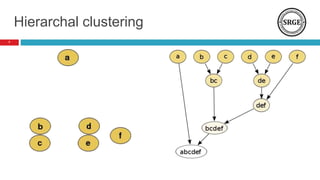
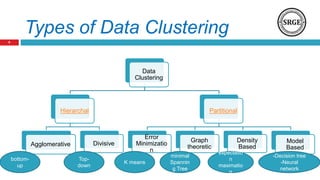
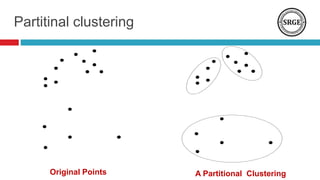
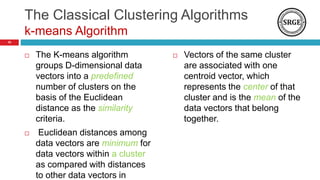
The document provides an overview of data clustering techniques, focusing on classical algorithms and the application of swarm intelligence (SI) algorithms. It discusses the role of clustering in various fields and introduces several SI methods, such as ant colony and particle swarm optimization, which can enhance clustering performance. The potential improvements over traditional methods, such as refining cluster quality and determining optimal cluster centers, are also highlighted.