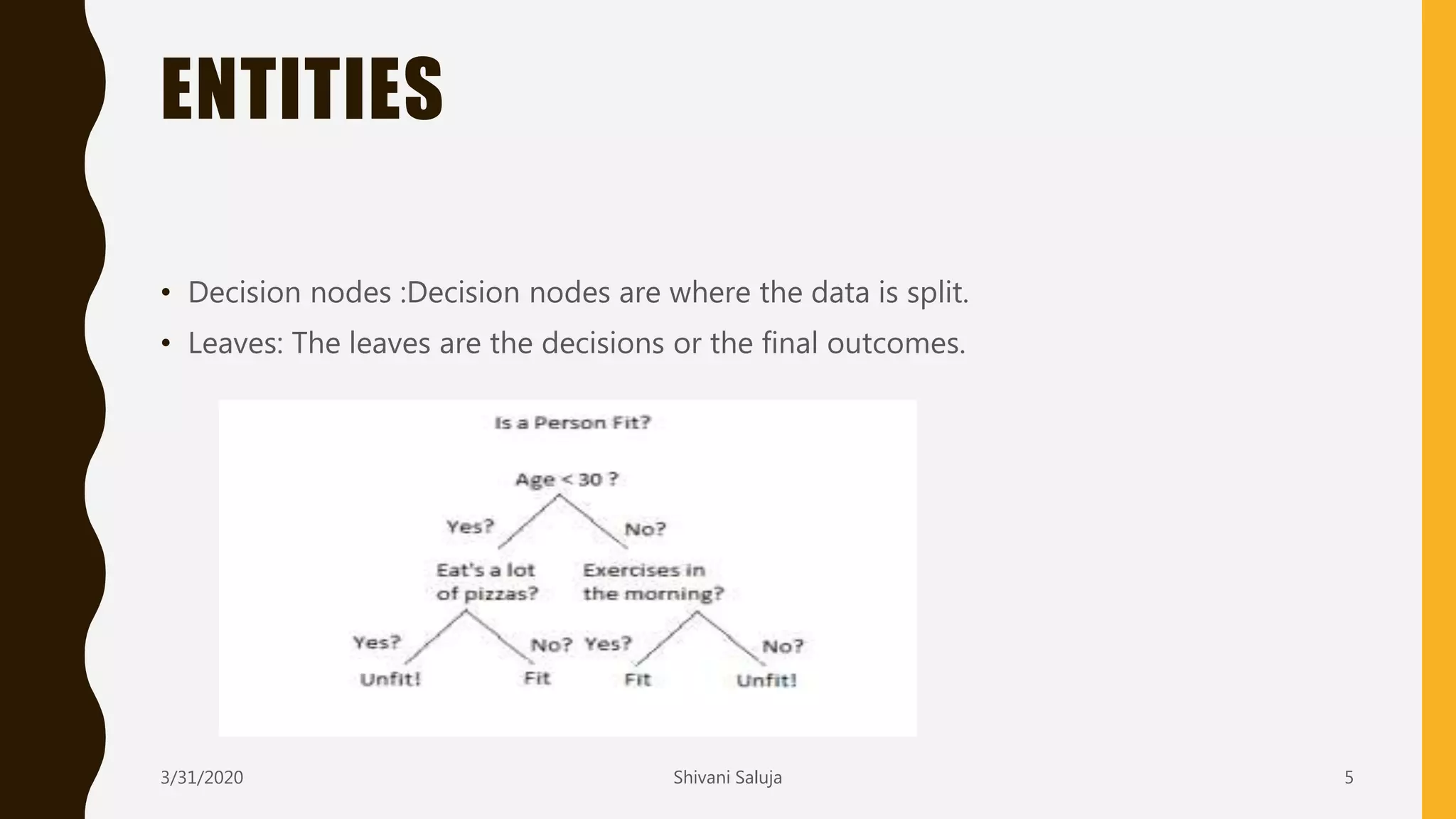
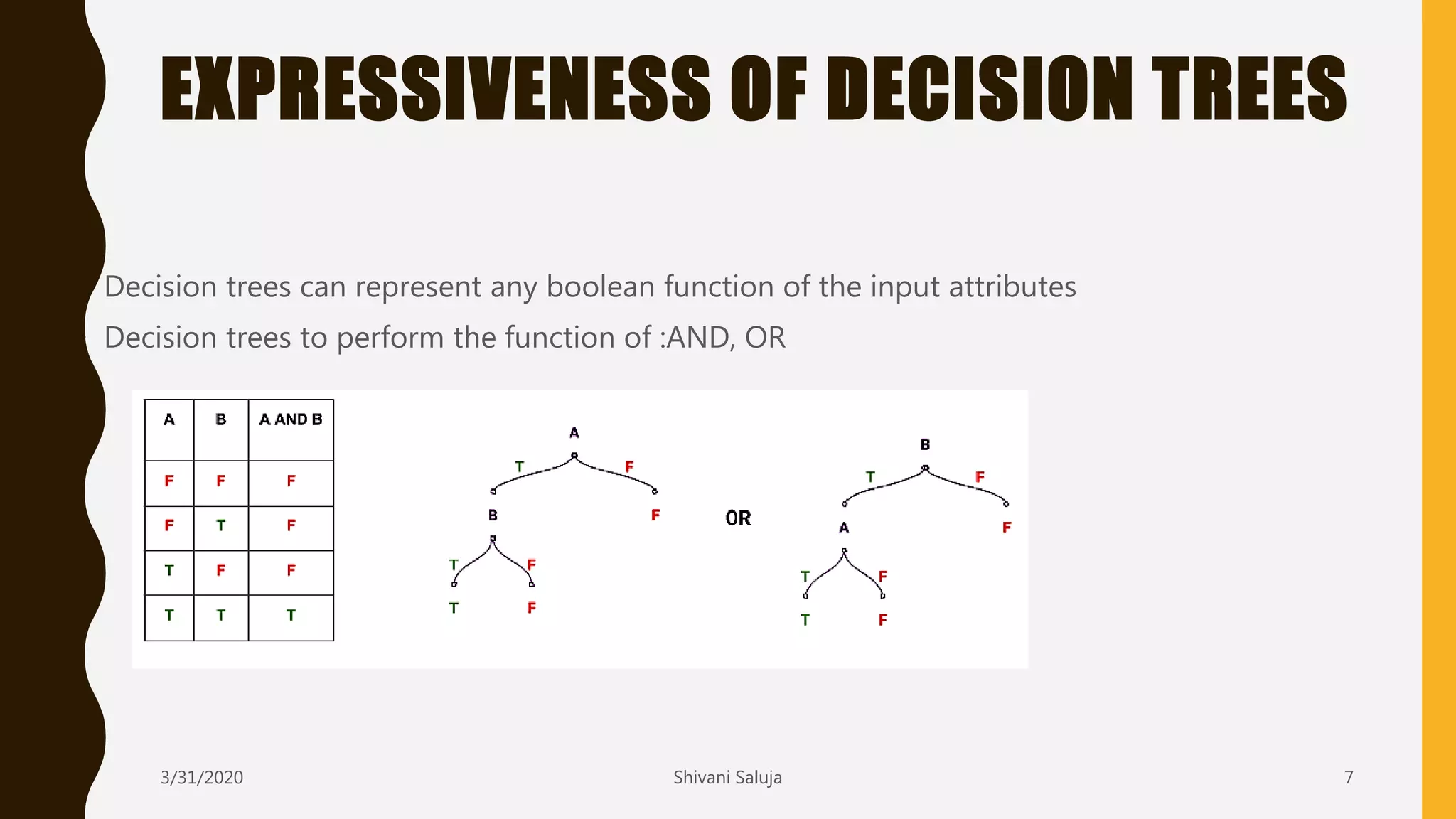
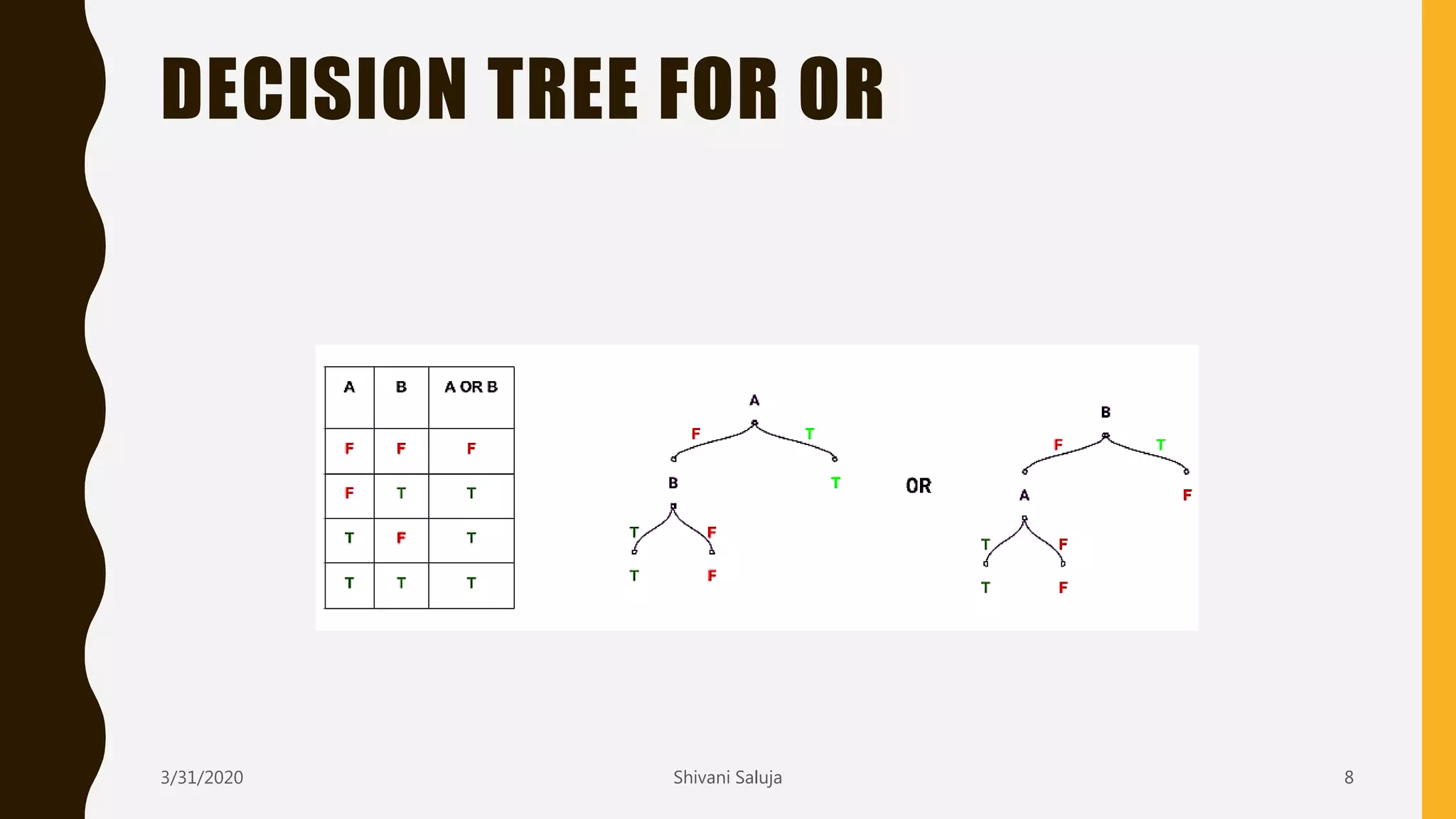
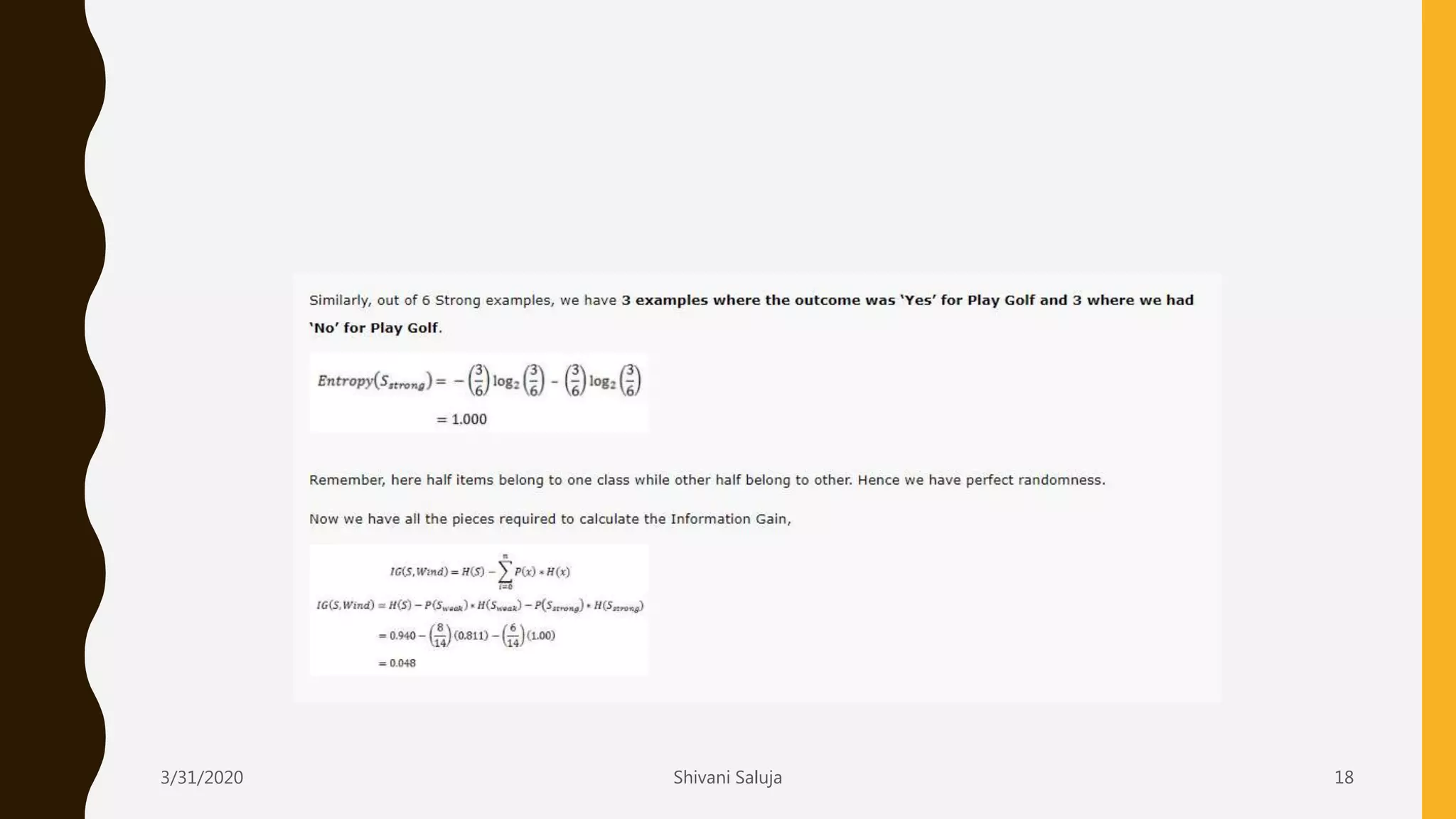
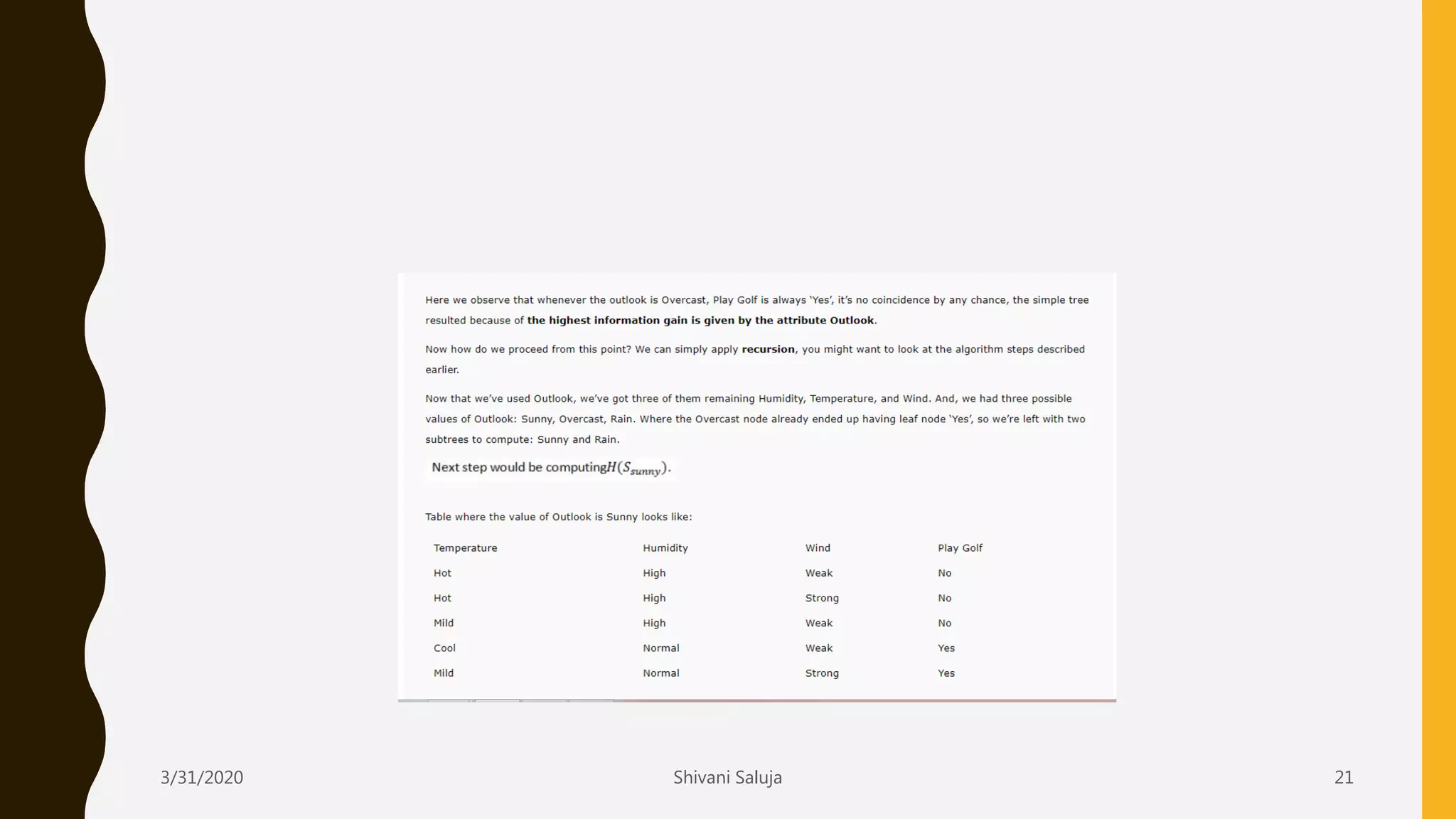
Decision trees are a type of supervised machine learning that use a tree-like model to predict target variables. They work by splitting data into smaller and smaller groups (branches) based on attribute values, continuing until the groups only contain similar target variable values or cannot be split further. The tree consists of decision nodes that test attributes, branches representing the outcome of the tests, and leaf nodes that represent classifications or predicted target values. The ID3 algorithm builds decision trees by selecting the attribute that creates the most information gain at each split in a greedy, top-down manner.