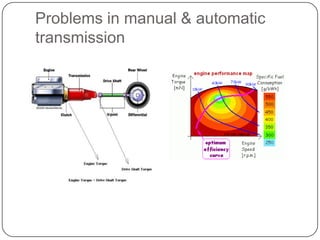
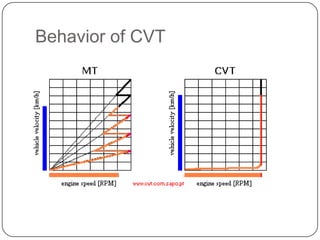
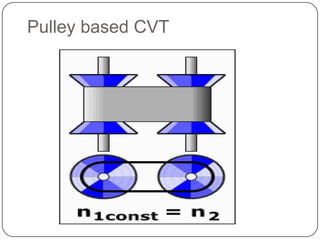
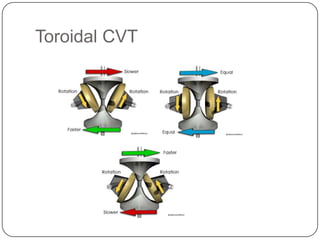
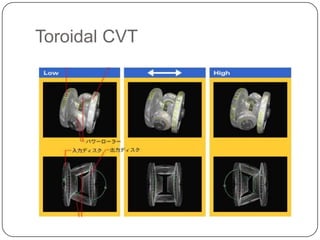
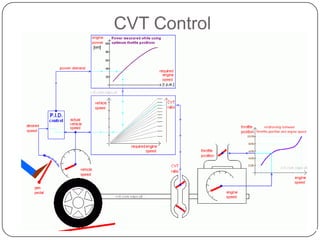
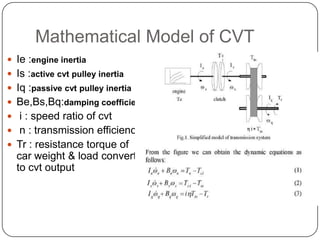
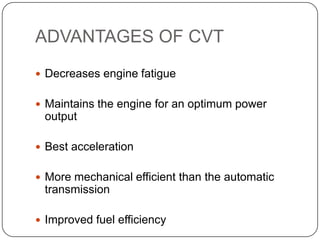
This document discusses continuous variable transmissions (CVTs). It begins by explaining the basic function of a transmission to change the speed ratio between an engine and wheels. It then discusses problems with manual and automatic transmissions. CVTs are introduced as having benefits like providing optimal engine torque, no shift clunk, continuous ratio adjustment, better acceleration, and improved fuel efficiency. The main types of CVTs are then outlined as pulley-based, toroidal, and hydrostatic. Details are provided on the mechanisms and operation of each type. Control and modeling of CVTs are also briefly covered. Advantages are said to include decreased engine fatigue and improved efficiency over automatic transmissions, while disadvantages include limited torque and higher cost