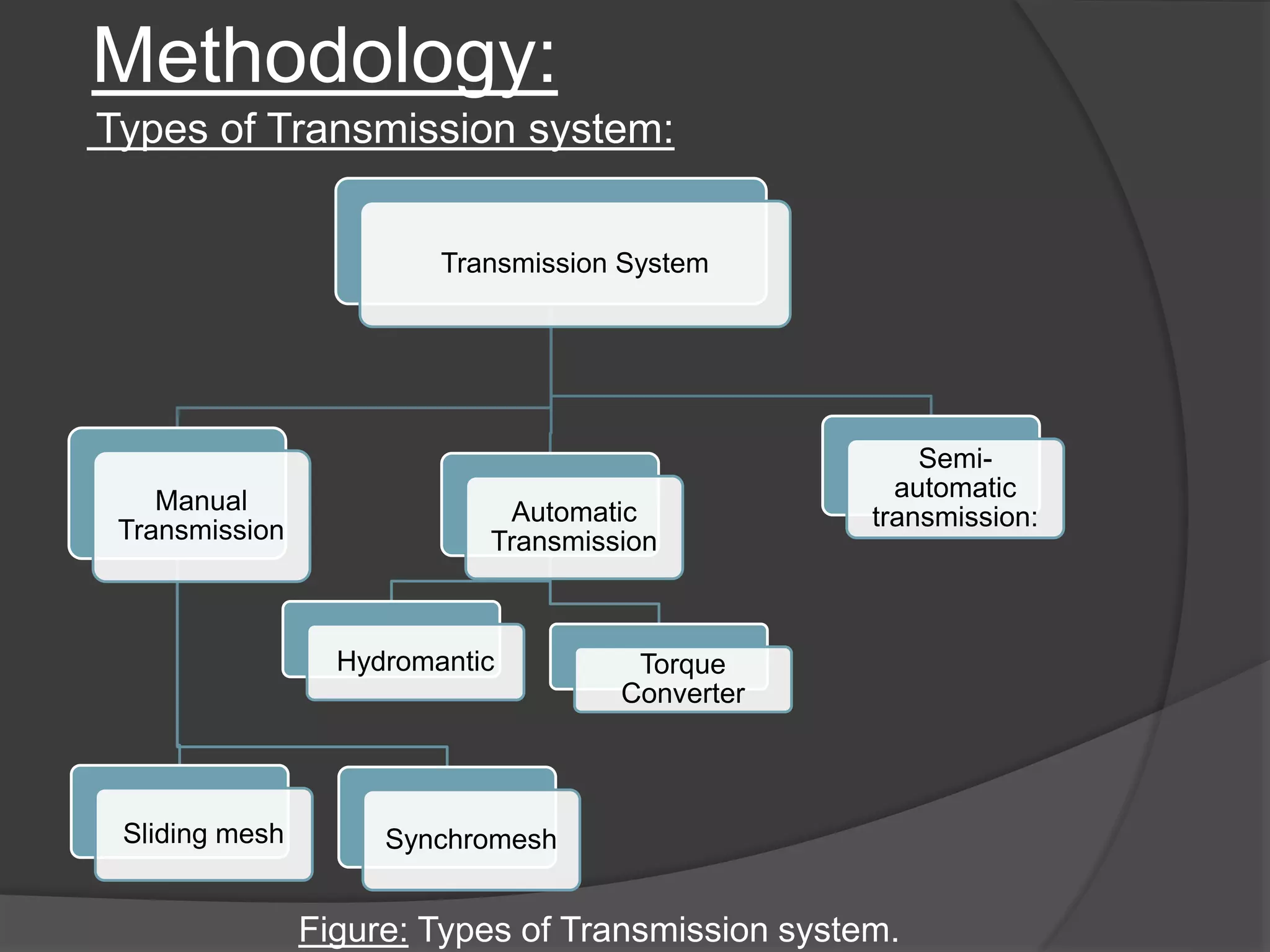
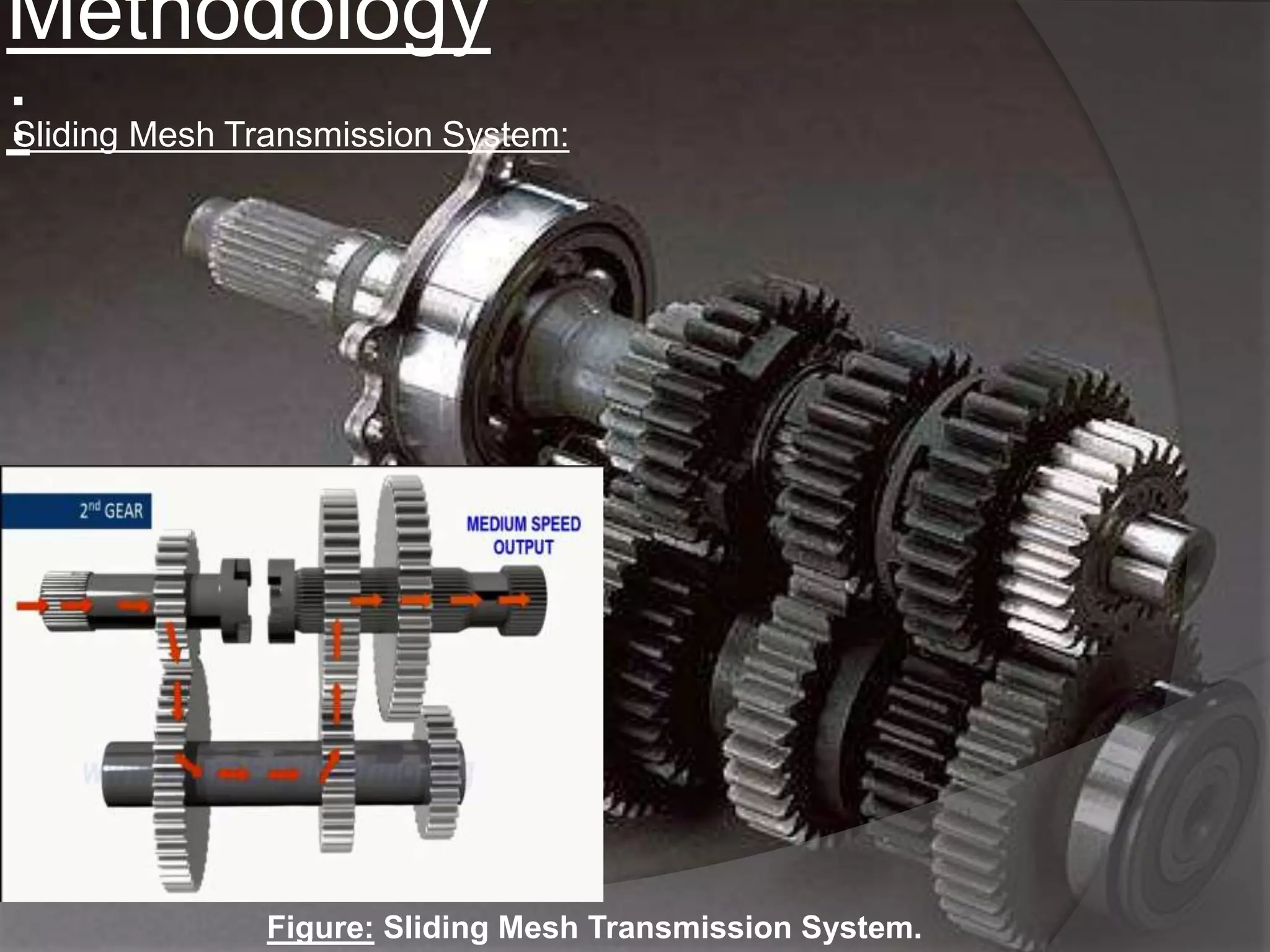
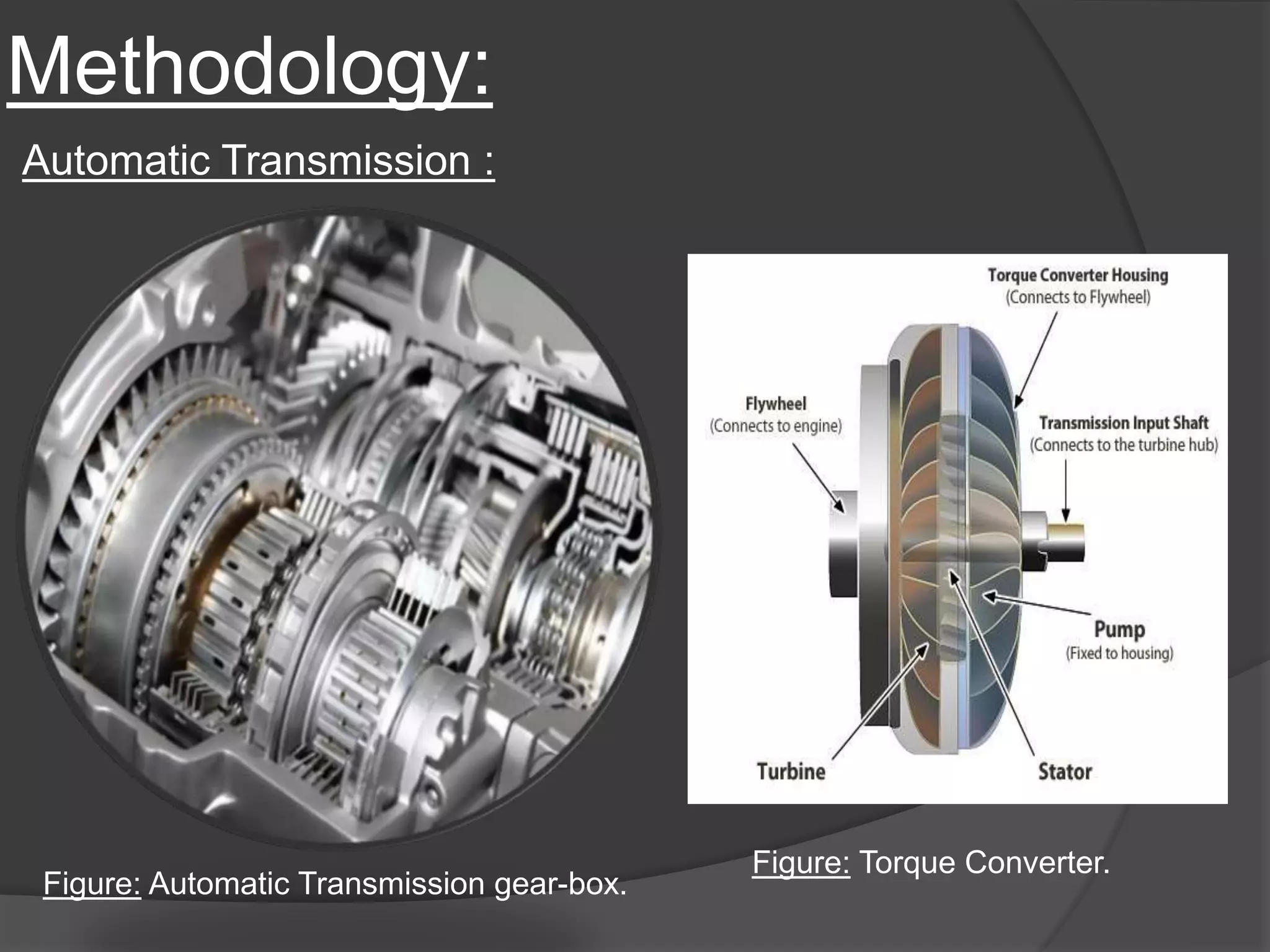
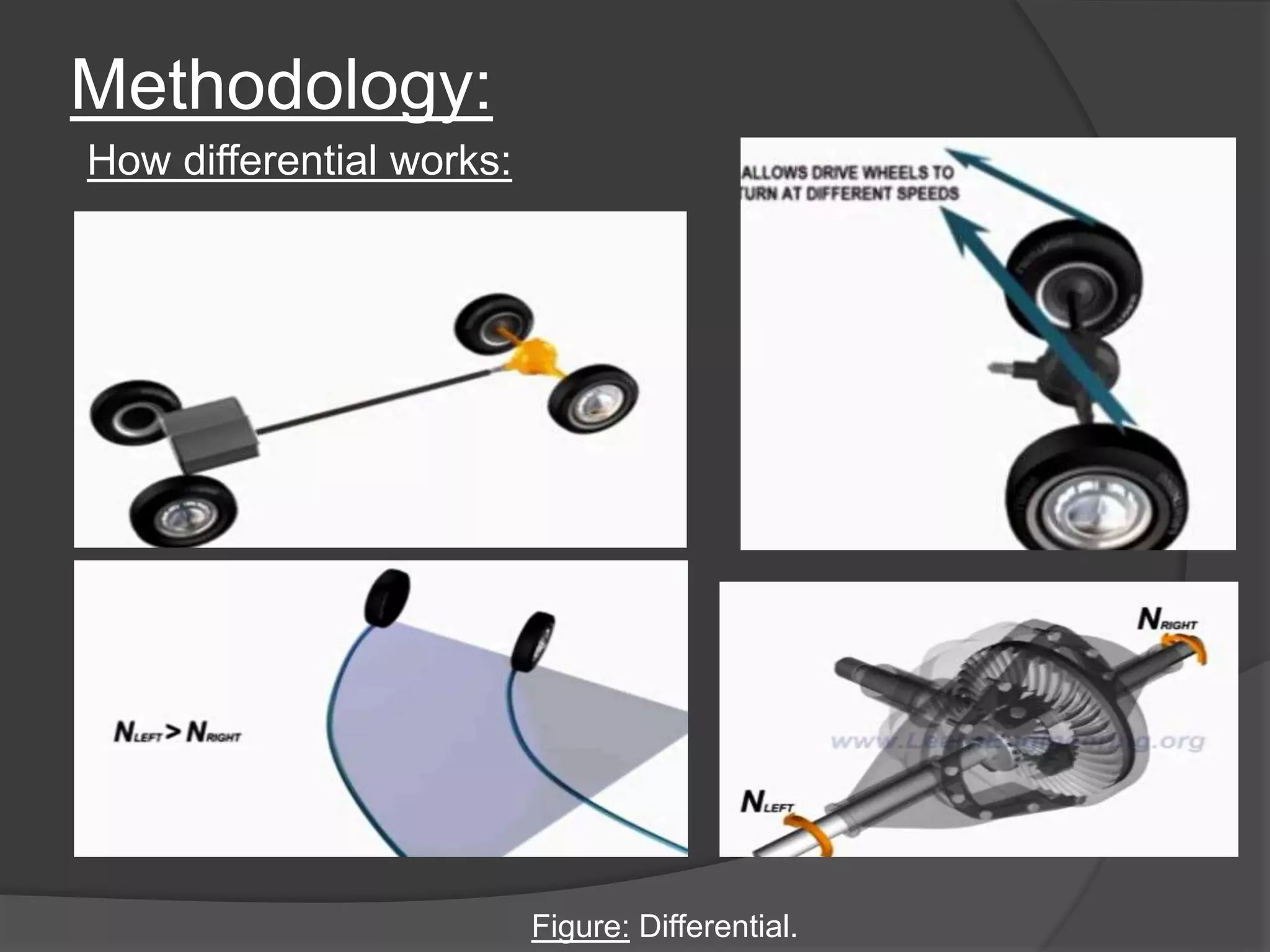
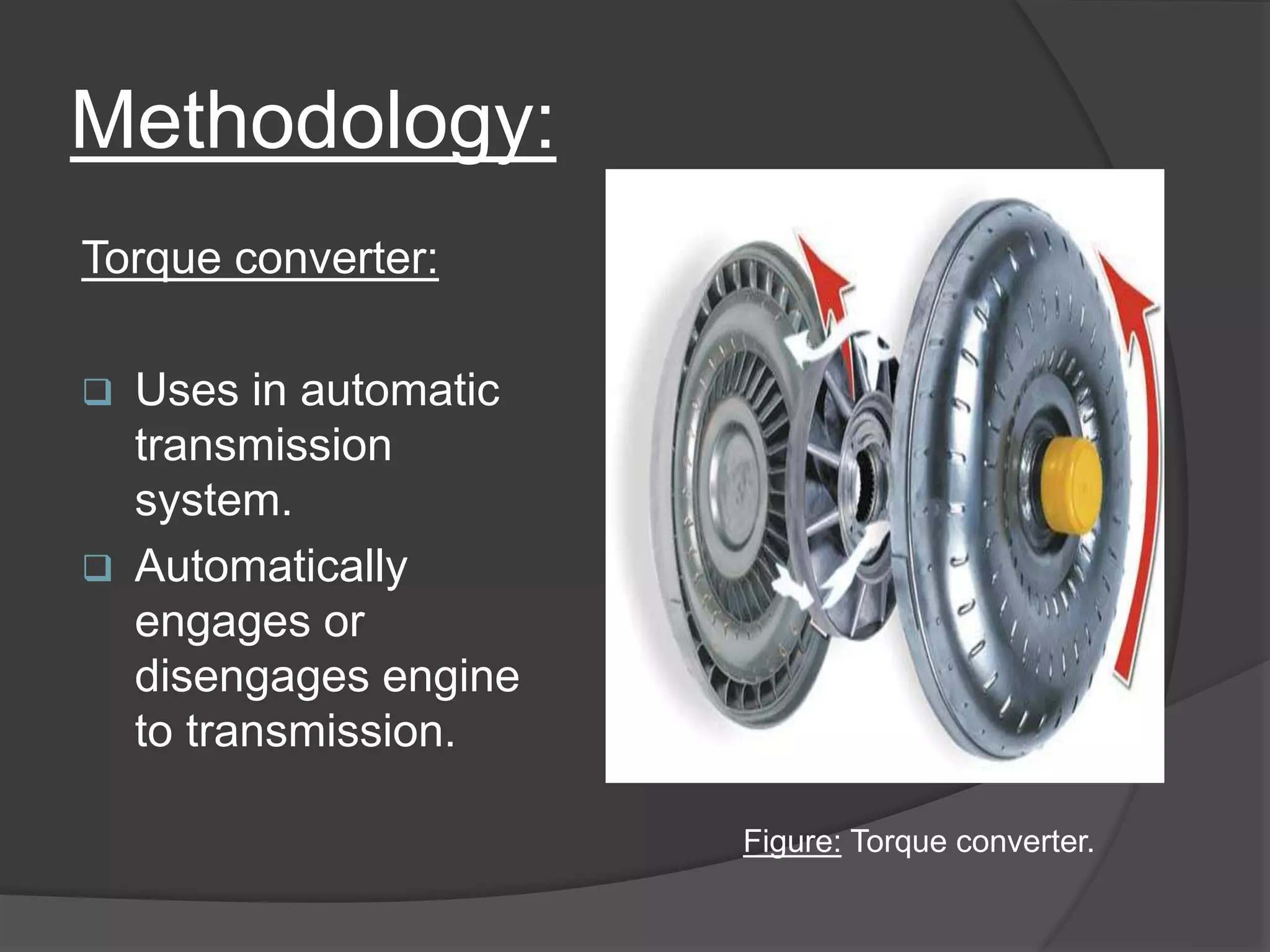
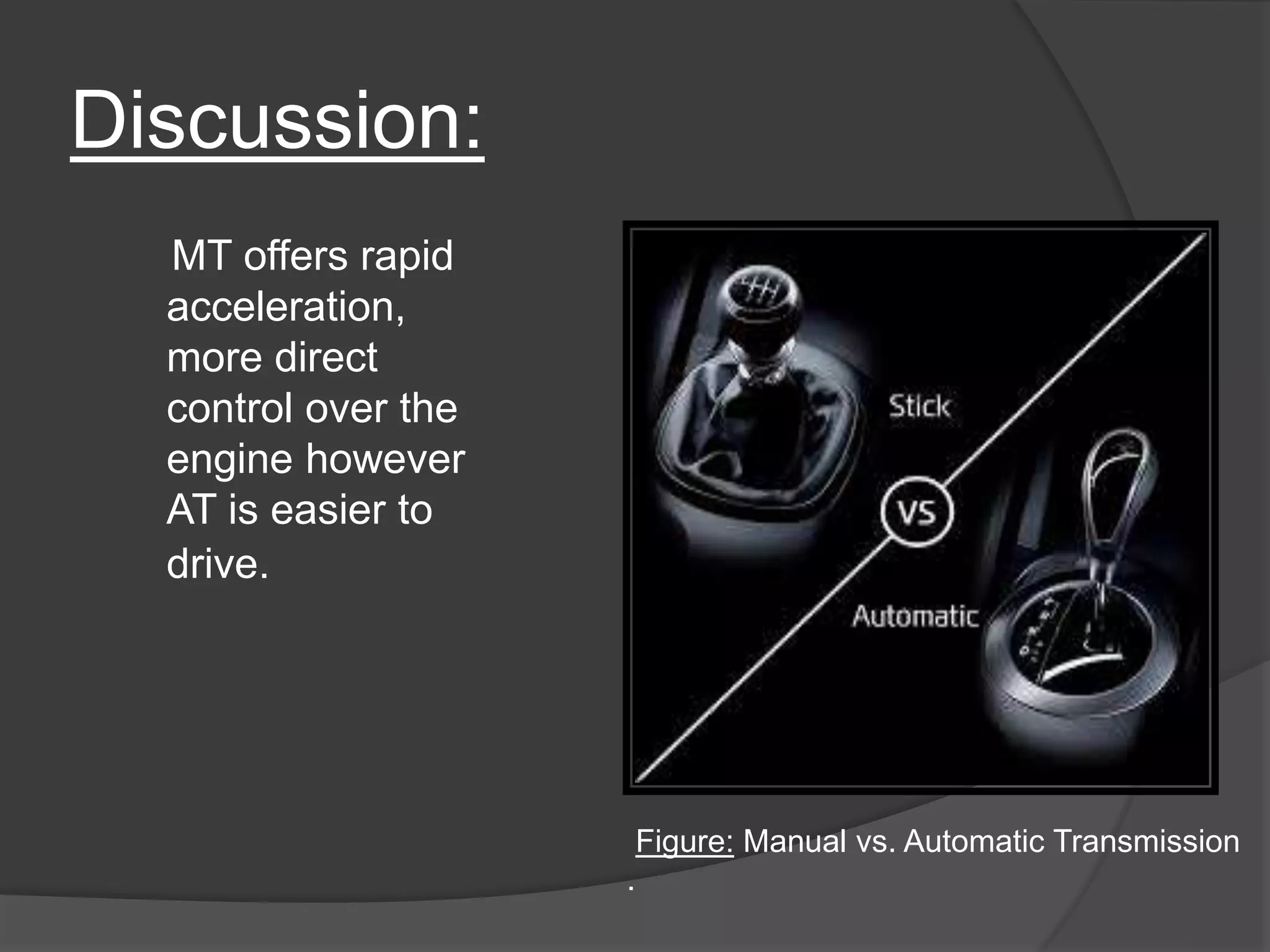
The document discusses the transmission system in vehicles, outlining its purpose of transmitting mechanical power from the engine to the wheels. It covers various types of transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, and continuously variable transmissions, detailing their components and functioning. The conclusion suggests that significant changes are anticipated in the automotive industry based on the findings of this study.