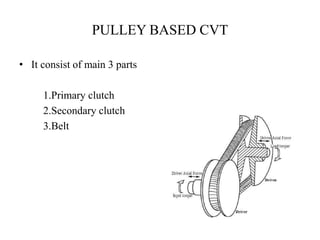
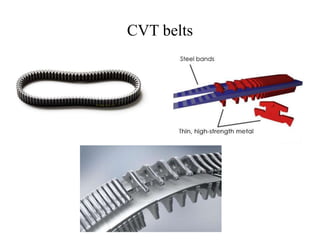
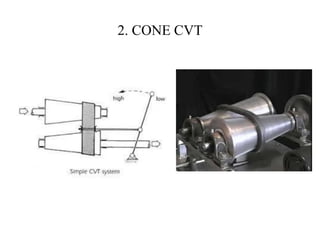
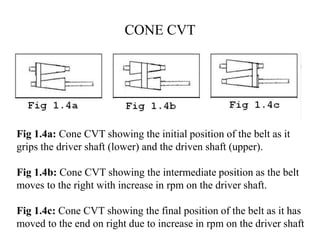
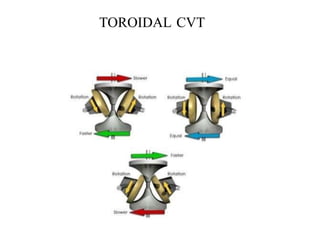
This document provides an overview of continuously variable transmissions (CVTs). It discusses the history and development of CVTs, the main types including pulley-based, cone, toroidal, and hydraulic CVTs. The advantages of CVTs are allowing the engine to run at an ideal RPM regardless of vehicle speed and fewer moving parts compared to automatic transmissions. Disadvantages include limited torque capacity and higher cost compared to manual transmissions. CVTs are commonly used in automobiles and are being developed for other applications like trucks, buses, and wind turbines.