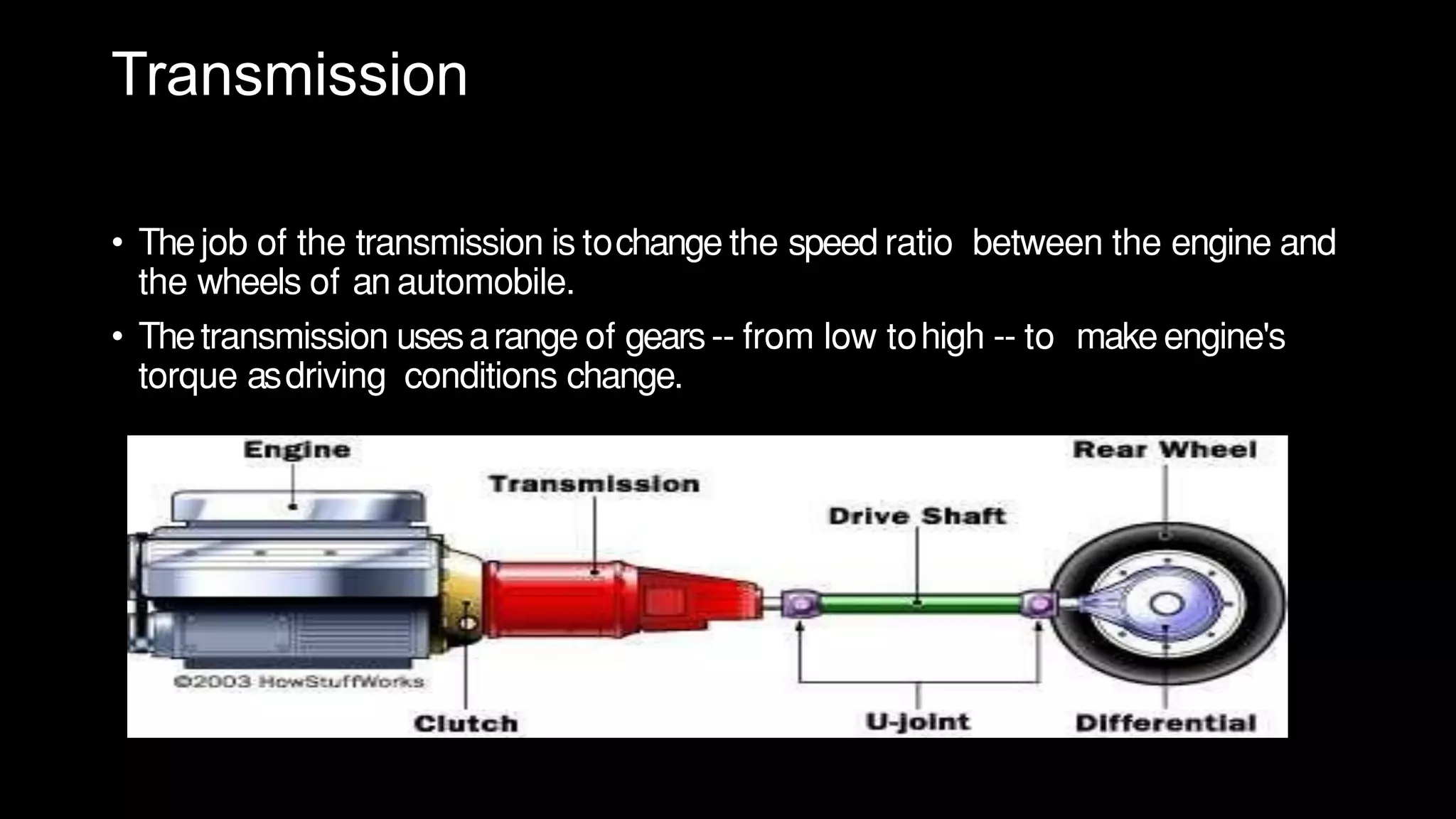
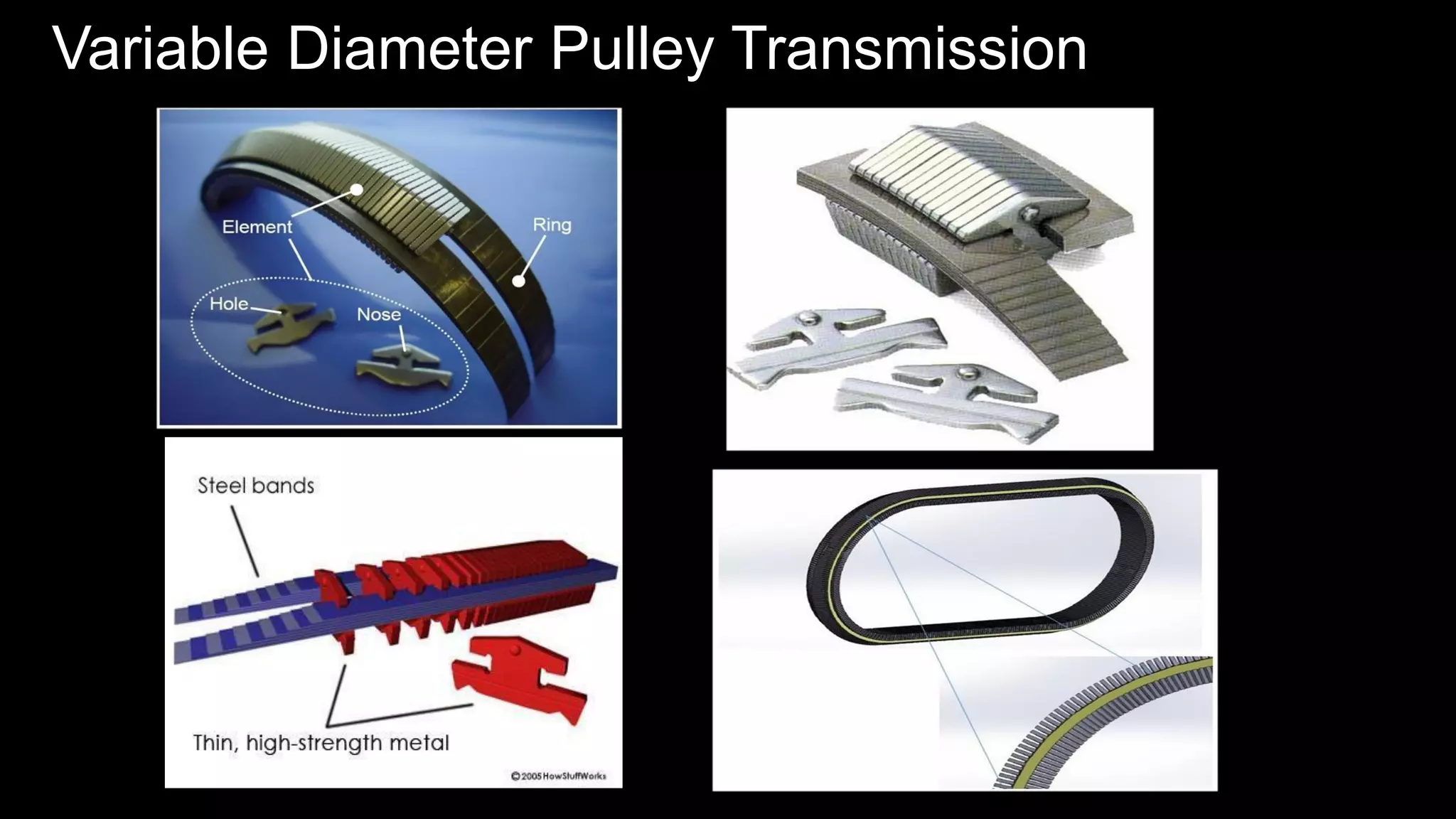
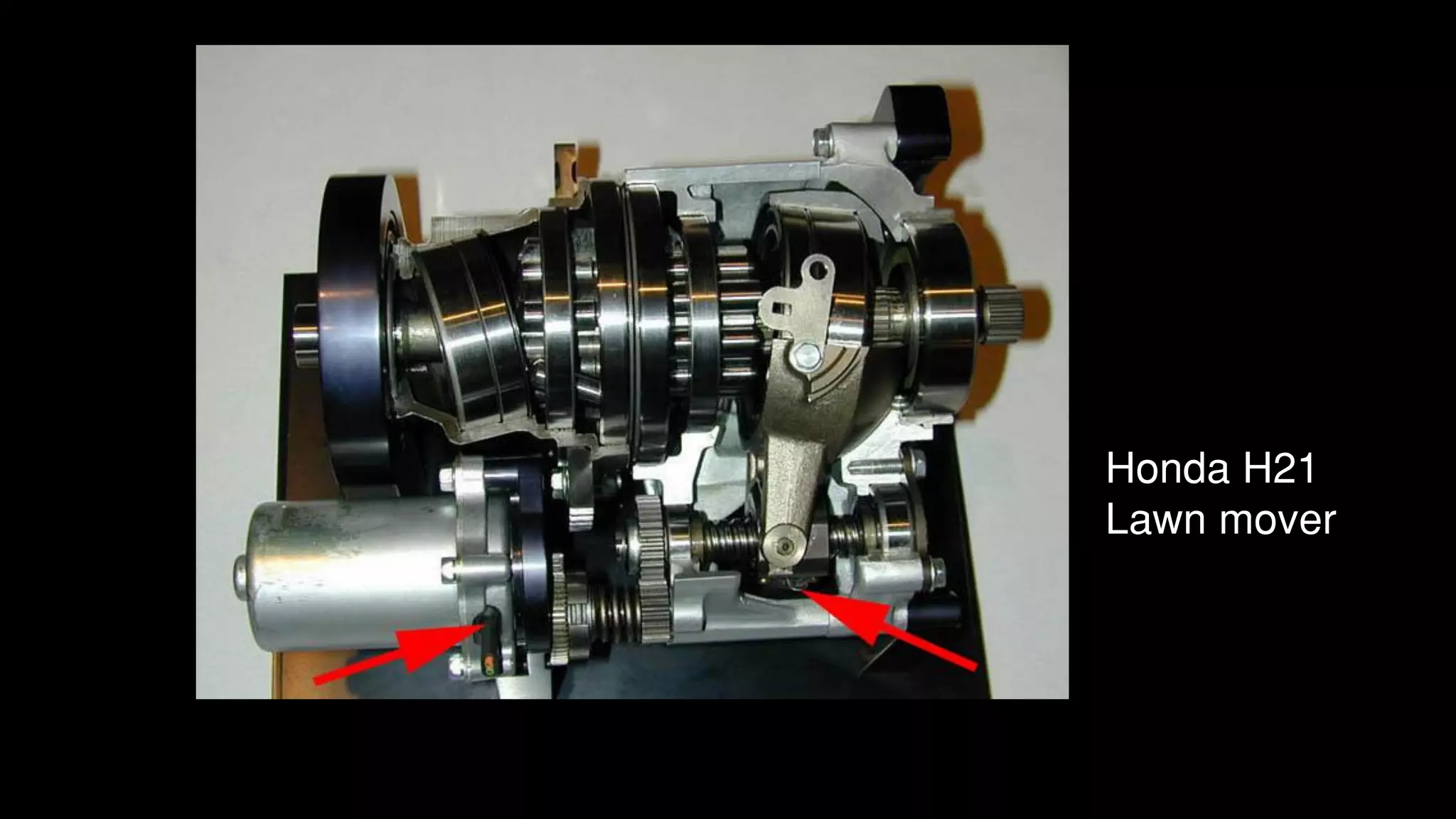
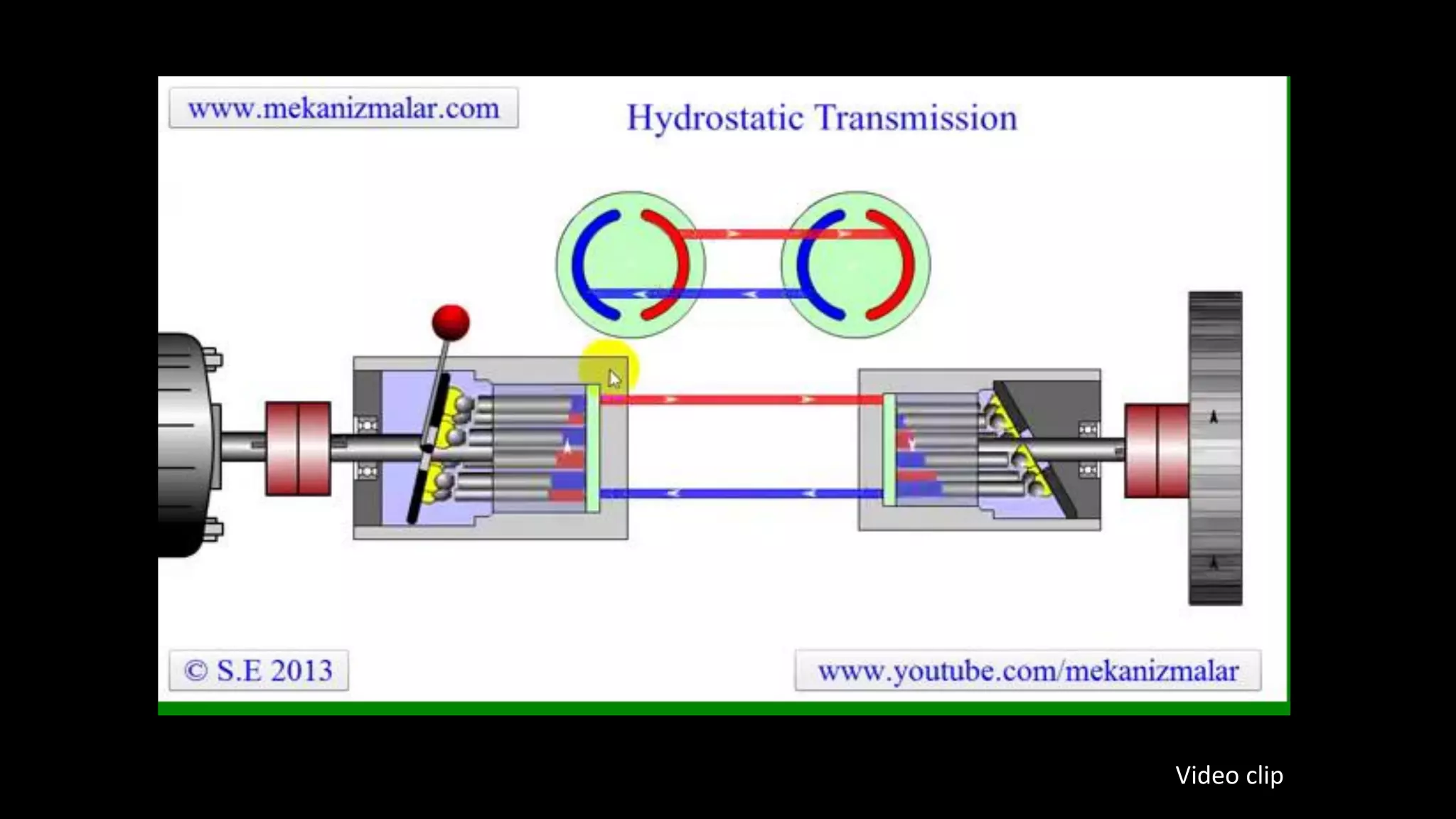
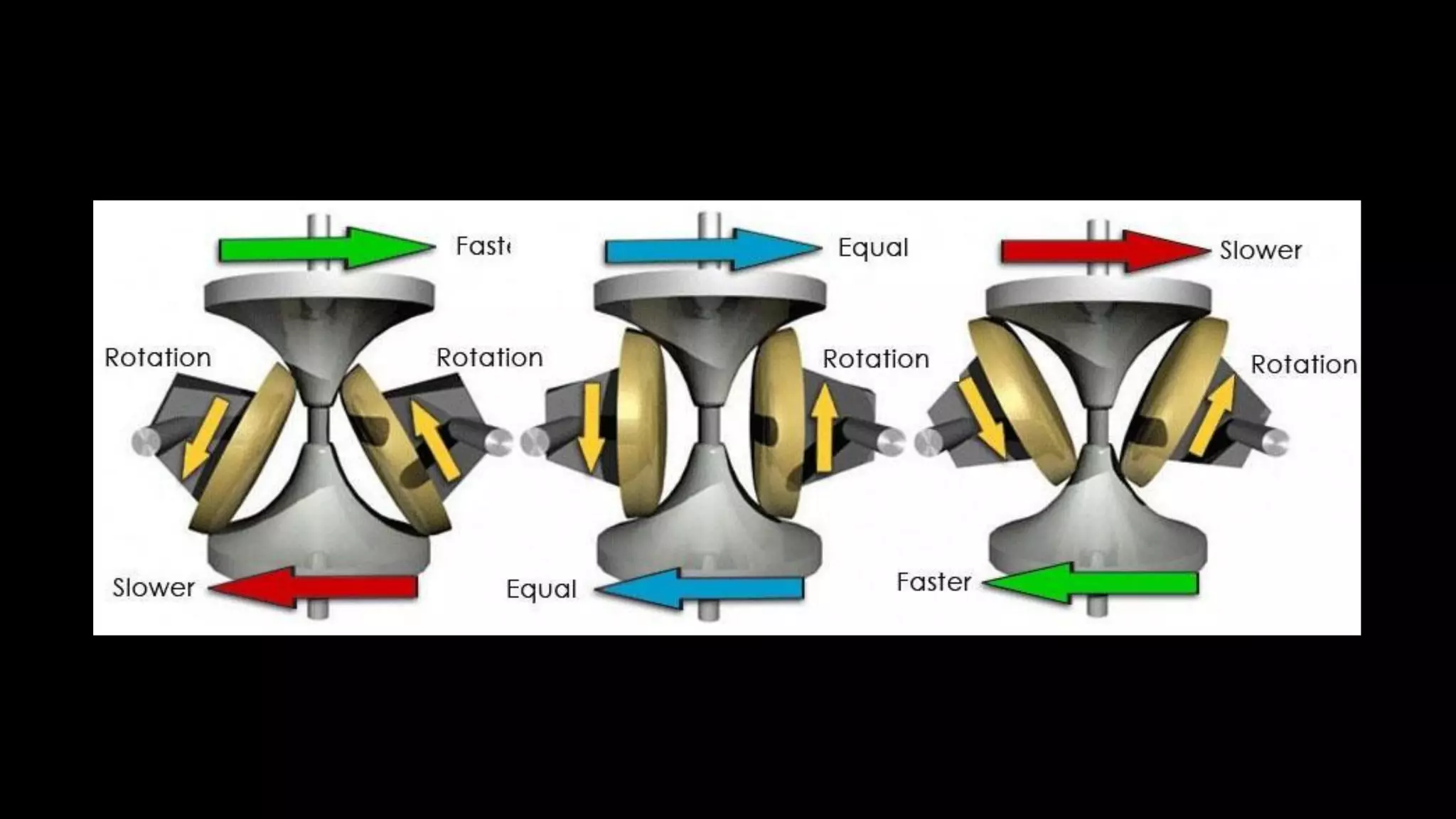
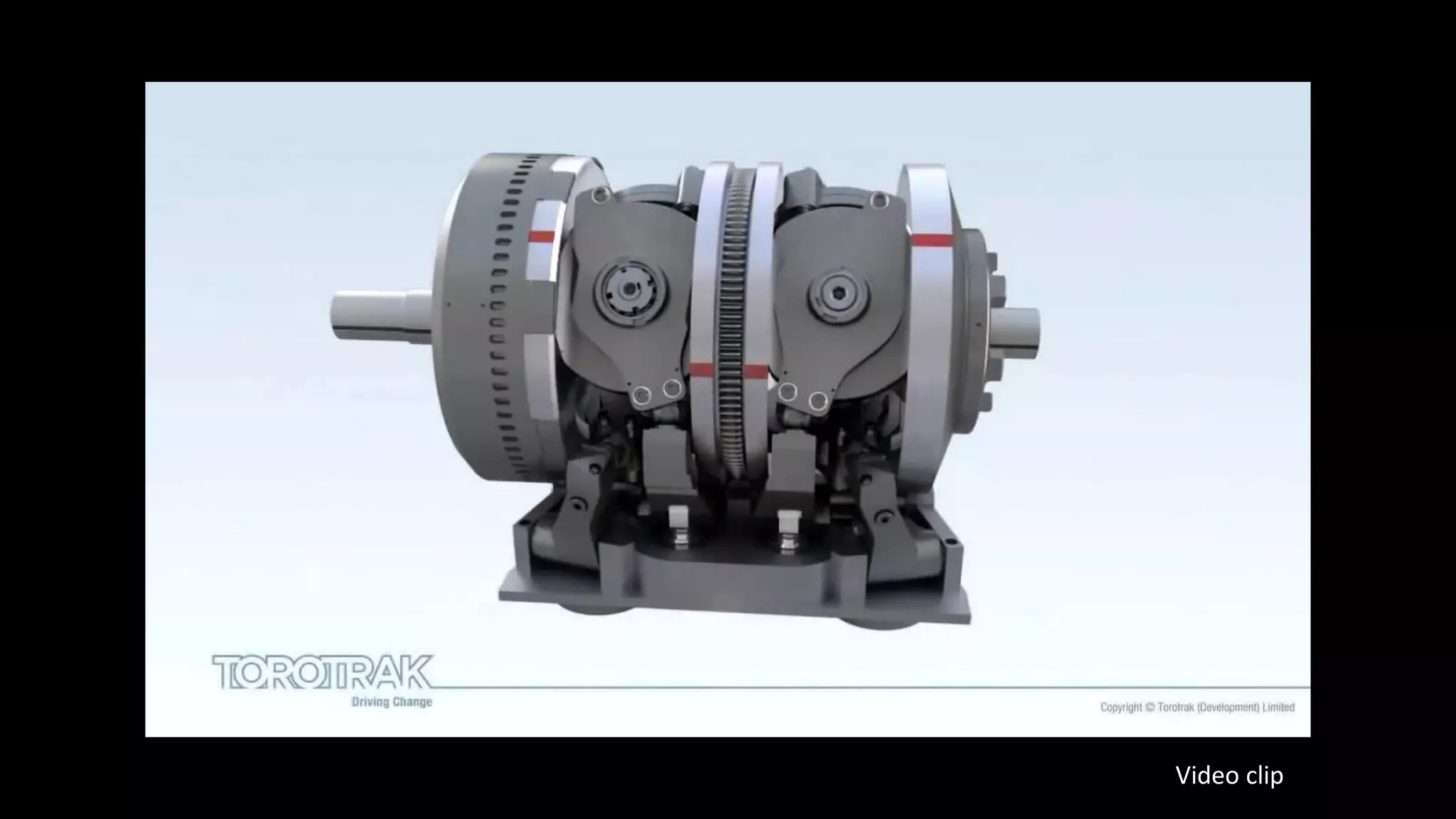
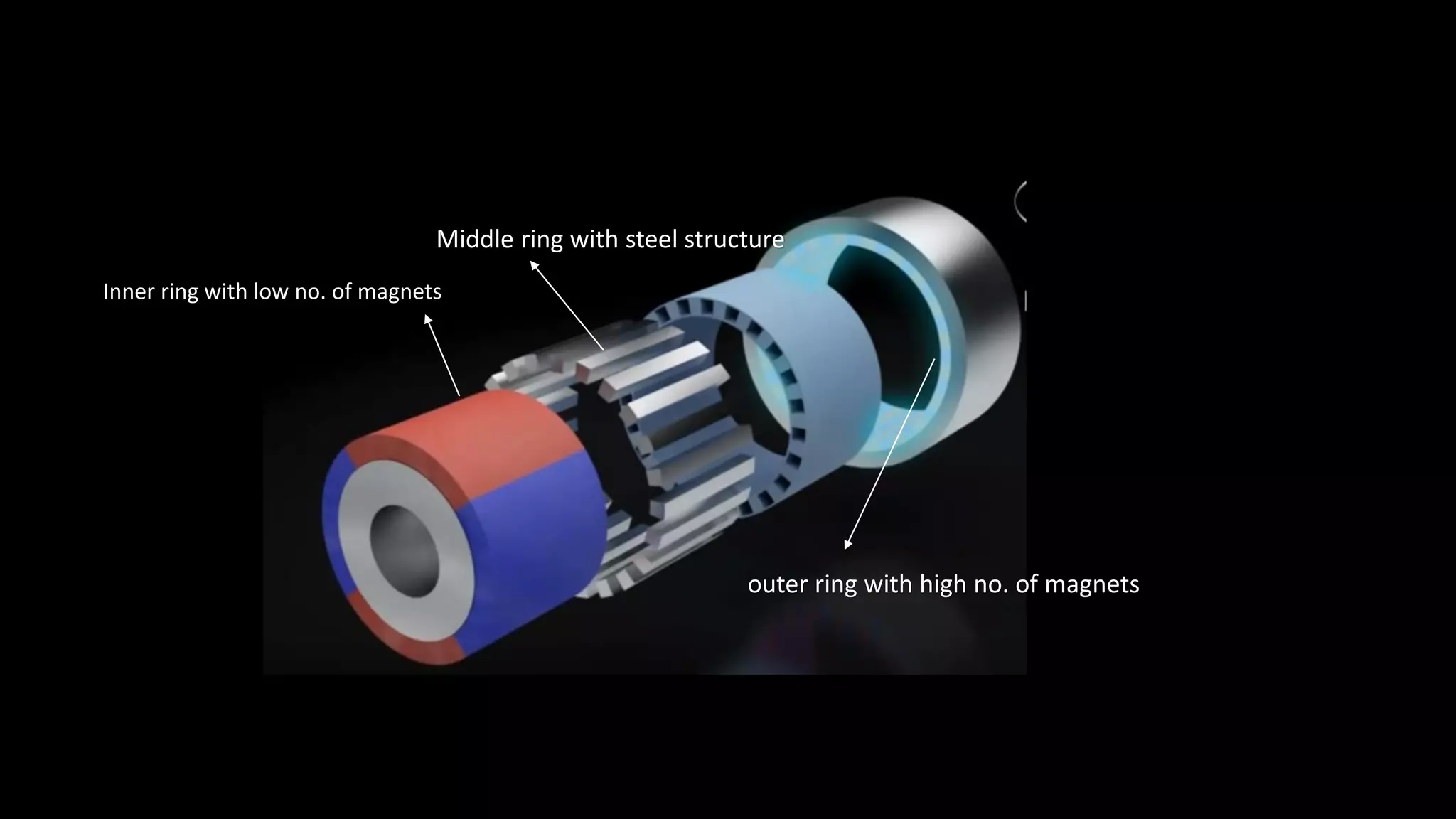
This document provides an overview of continuously variable transmission (CVT), detailing its components, working principles, timeline, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. CVTs offer smooth operation with infinite gear ratios, although they face challenges in transmitting high torque at low speeds. The technology is impacting automotive efficiency and emissions, with innovations from various manufacturers enhancing its application.