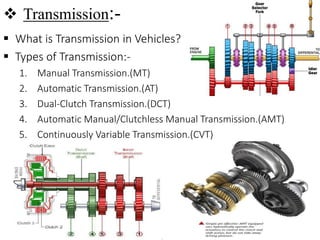
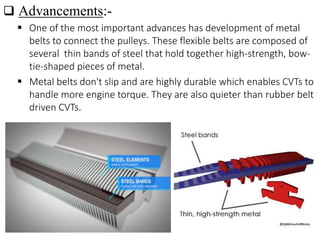
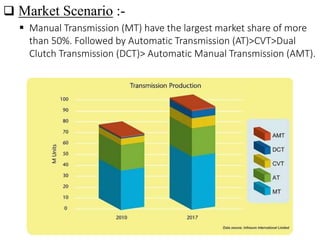
This document provides an overview of continuously variable transmissions (CVTs). It discusses the history of CVTs, how they work using a belt-pulley system to provide infinite gear ratios, and their advantages like improved fuel efficiency. The document also outlines different types of CVTs, applications, and the current market share of various transmission types. CVTs are becoming more common in small cars and SUVs due to their improved performance and efficiency compared to traditional automatic transmissions.