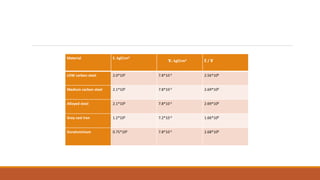
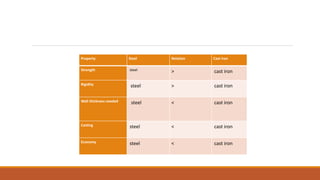
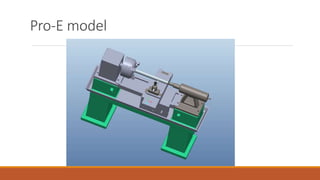
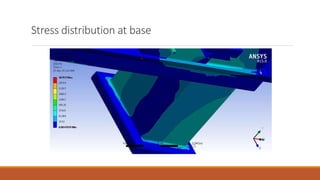
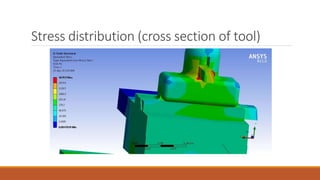
This document summarizes the design and analysis of a lathe machine. It describes the materials selected for different parts of the lathe based on their properties like strength, rigidity, and economy. It then outlines the specifications of the lathe model created in Pro-E, including dimensions and maximum workpiece size. Cutting forces acting on the tool for a given depth of cut and feed rate are calculated. A static structural analysis of the lathe assembly is performed in ANSYS to determine stress distributions in parts like the tool, base, tail stock, and at interfaces. The analysis shows stresses and deformations are within allowable limits.