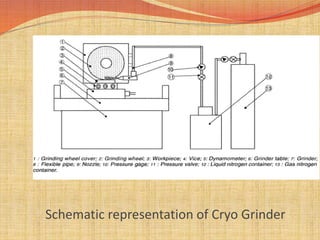
Cryogenics is the study of very low temperatures, including temperatures below -150°C that can be attained using cryogenic liquids like liquid nitrogen and liquid helium stored in Dewar flasks. Some key applications of cryogenics discussed include cryogenic rocket engines, which provide high energy per unit mass and were pioneered by the US and India. Cryogenic grinding is also discussed as an application, which avoids problems with heat generation, tool wear, and oxidation seen in conventional grinding. Both advantages like lower grinding costs and finer particle sizes, and disadvantages like high operating costs are reviewed. Health hazards associated with cryogenic liquids like frostbite and cold embrittlement are also summarized.