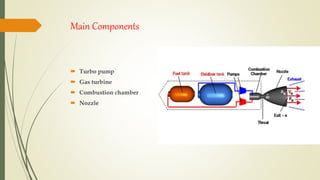
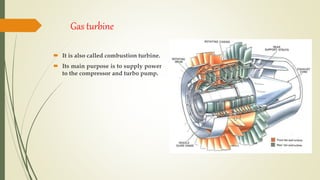
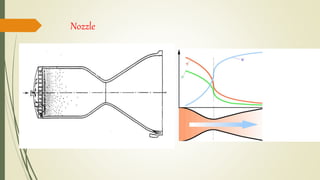
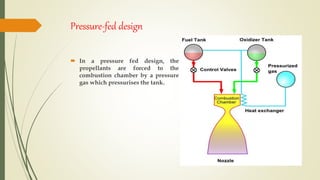
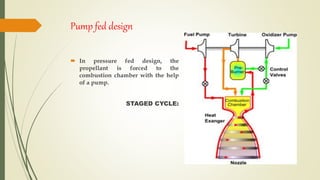
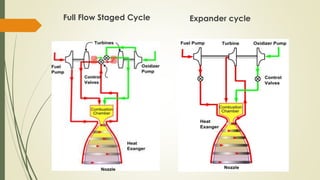
The document discusses cryogenic engines, focusing on their components, design, and operational procedures, including advantages and disadvantages. It highlights the history of cryogenic engine development, with the first successful launch involving human spaceflight in 1987. The conclusion emphasizes the efficiency of cryogenic engines over traditional propulsion systems.