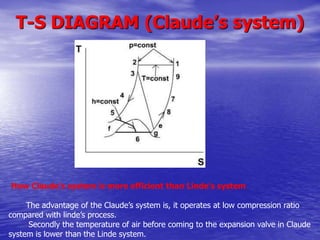
Cryogenics involves reducing the temperature of components to extremely cold levels, usually below -250°C. There are two main methods for producing cryogenic temperatures - Linde's system and Claude's system, which both use compression and expansion of gases. Cryogenics has applications in aerospace, medicine, manufacturing, and electronics. In aerospace, cryogenic engines use liquid hydrogen and oxygen as propellants. In medicine, cryosurgery uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissue. Manufacturing uses cryogenic treatment to improve tool durability. Electronics utilizes cryogenics to enable superconducting devices.



![TYPES OF CRYOGENIC TREATMENT
• SHALLOW CRYOGENICS, made the objects to temperature of approximately -
120o F.
• FLOODING, takes the component to -120o F, then the chamber is flooded with
liquid nitrogen.
• DEEP CRYOGENICS TREATMENT, Subjects the objects to the temperature of
approximately -300o F.
ABSOLUTE ZERO
Absolute zero is a temperature marked by a 0 entropy configuration. It is the coldest
temperature theoretically possible and cannot be reached by artificial or natural
means. Temperature is an entropically defined quantity that effectively determines
the number of thermodynamically accessible states of a system within an energy
range. Absolute zero physically possesses quantum mechanical zero-point energy.
Having a limited temperature has several thermodynamic consequences; for
example, at absolute zero all molecular motion does not cease but does not have
enough energy for transference to other systems, it is therefore correct to say that at
0 Kelvin molecular energy is minimal. In addition, any particle with zero energy
would violate Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle, which states that the location and
momentum of a particle cannot be known at the same time. A particle at absolute
zero would be at rest, so both its position, and momentum (0), would be known
simultaneously.
• By international agreement, absolute zero is defined as precisely 0 K on the Kelvin
scale, which is a thermodynamic (absolute) temperature scale, and −273.15° on the
Celsius scale.[1] Absolute zero is also precisely equivalent to 0 R on the Rankine
scale (same as Kelvin but measured in Fahrenheit intervals), and −459.67° on the
Fahrenheit scale.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryogenics-230817042221-b2c52a0e/85/Cryogenics-ppt-4-320.jpg)







![CRYOGENIC ENGINES IN AEROSPACE
• The first operational Cryogenic Rocket Engine is the 1961 NASA design the
RL-10 LOX LH2 rocket engine.
• The upgraded cryogenic second-stage Pratt & Whitney RL10B-2 engine is
based on the 30-year heritage of the reliable RL10 engine.
• At Mahendragiri in Tamil Nadu, is the Liquid Propulsion System Centre
[LPSC]. Here work on developing India’s own cryo - engines has been
quietly moving. The system involves materials working at 250 deg below
zero and pumps at speeds of 40,000 rpm. There are also complex metering,
monitoring, integrating technologies involved. The engines are required to
fire for about 700 seconds during the final stage of a launch providing 7
tones of thrust..
• The Engine works on ‘Staged Combustion Cycle’ with an integrated turbo
pump running at around 42,000 rotations per minute (rpm). It is also
equipped with two steering engines developing a thrust of 2 kN each to
enable three-axis control of the launch vehicle during the mission. Another
unique feature of this engine is the closed loop control of both thrust and
mixture ratio, which ensures optimum propellant utilization for the mission.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryogenics-230817042221-b2c52a0e/85/Cryogenics-ppt-13-320.jpg)







