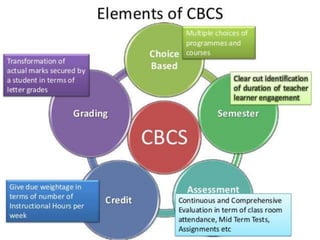
1. The document discusses credit and semester systems in higher education, including definitions of key terms like credit, semester, choice based credit system (CBCS), and credit based semester system (CBSS).
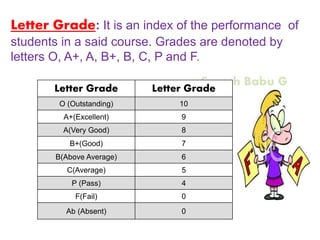
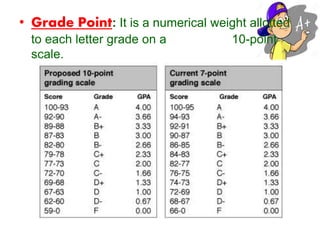
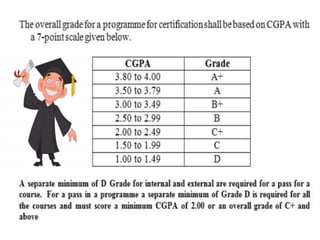
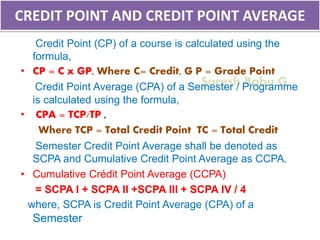
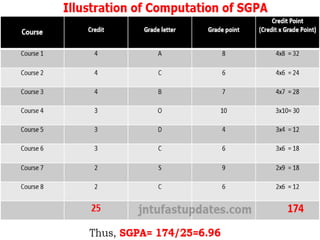
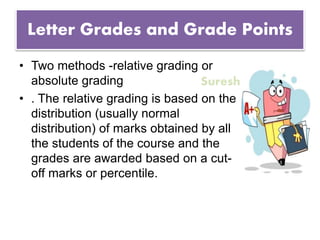
2. It explains how credits are used to measure student workload and learning outcomes, and how grade points and letter grades are assigned to evaluate student performance in courses.
3. The summary also provides an overview of the benefits of academic credit systems, which include keeping track of student progress, determining degree requirements, and estimating program workload.