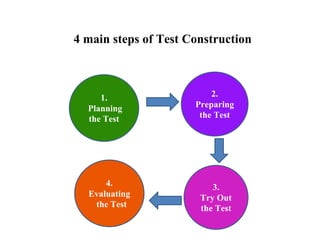
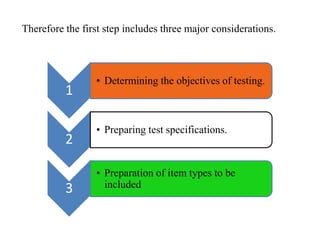
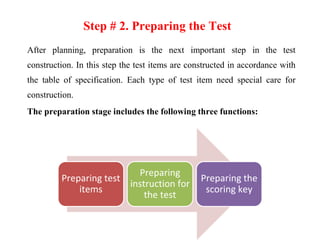
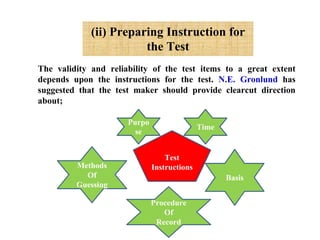
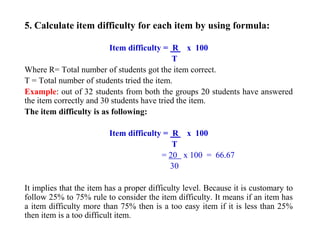
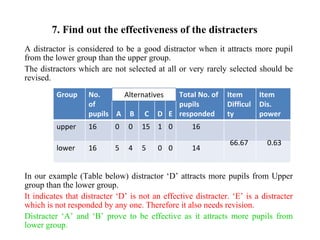
The document outlines the steps and principles involved in test construction within the educational field, emphasizing the importance of valid and reliable assessments. It details a systematic approach, including planning, preparing, trying out, and evaluating tests to ensure they measure educational objectives effectively. Key considerations such as test item development, instructions, scoring methods, and item analysis are highlighted to improve the quality and usability of assessments.

![Introduction
A test refers to a tool, technique or a method that is intended to measure students knowledge or their ability to
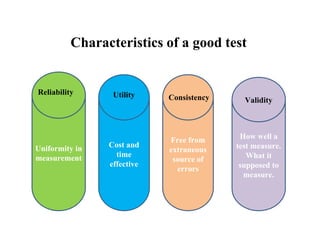
complete a particular task. In this sense, testing can be considered as a form of assessment. Tests should meet
some basic requirements, such as validity and reliability.
❖ testing is generally concerned with turning performance into numbers.
[Baxten,1998]
❖13% of students who fail in class are caused by faulty test questions.
[World watch- The philadelphia
trumpet, 2005]
❖ It is estimated that 90% of the testing items are out of quality.
[Wilen WW,1992]
❖ The evaluation of peoples progress is a major aspect of teachers job.
[Ornaldo & Antario, 1995]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/constructionoftest-220207124853/85/Construction-of-Test-2-320.jpg)