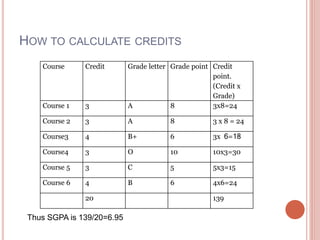
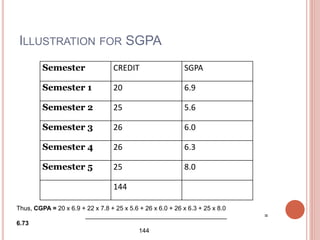
This document discusses course equivalency and credit systems for higher education. It defines key terms like course equivalence, college transfer, transcripts, course credits, and credit calculation. It provides details on credit systems in India, recommendations from the University Grants Commission on grading systems and credits, and formulas for calculating semester and cumulative grade point averages using course credits and grades. Examples are given to illustrate how to determine a student's SGPA and CGPA based on their coursework over multiple semesters.