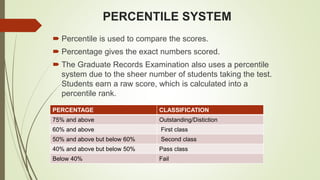
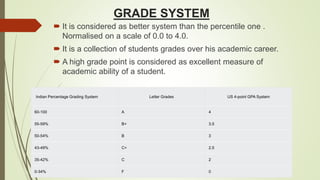
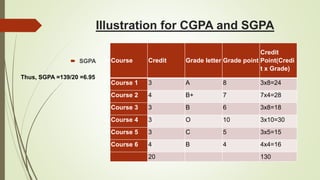
This document provides an overview and comparison of the percentile system and grade point average (GPA) system for assessing student performance. It then describes the key aspects of the Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) implemented in many Indian universities, including defining academic terms, how credits are assigned and counted, advantages like flexibility and disadvantages like workload. It also shows examples of computing semester GPA (SGPA) and cumulative GPA (CGPA) based on credits and letter grades earned in courses. The conclusion states that while it is still early, the CBCS aims to improve higher education quality through standardized grading across universities.