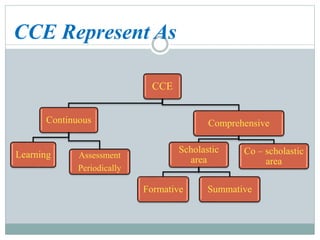
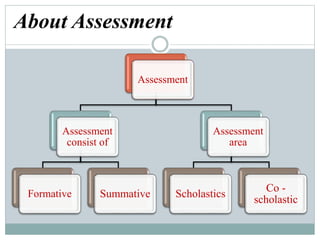
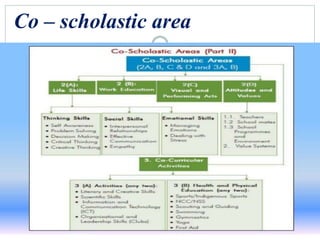
This document discusses continuous and comprehensive evaluation (CCE), including its aims, objectives, characteristics, and components. CCE aims to reduce student stress, make evaluation regular and comprehensive, and improve teaching and learning. It assesses students' scholastic development as well as co-scholastic areas like life skills, attitudes, interests, and physical health. CCE uses both formative and summative assessments periodically and continuously to evaluate students' cognitive, psychomotor, and affective development in a holistic manner. Progress reports are used to communicate student performance and guide future educational and career decisions.