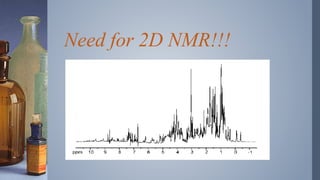
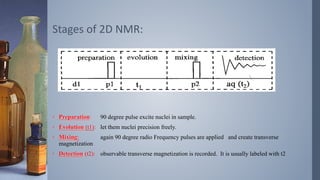
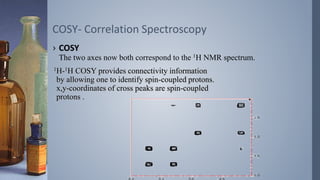
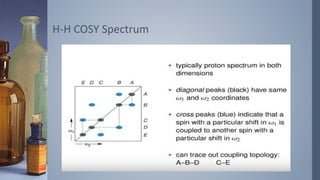
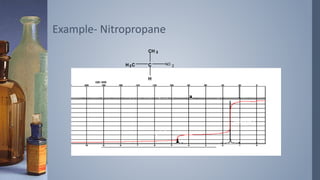
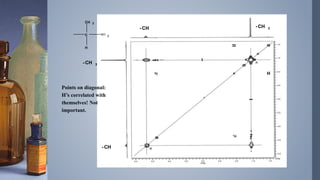
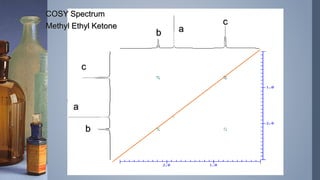
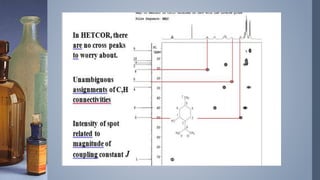
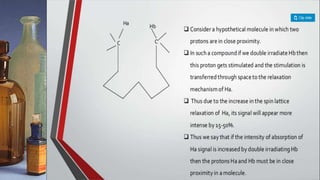
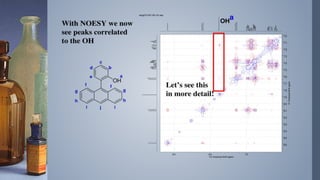
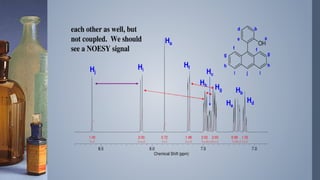
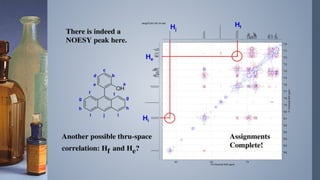
2D NMR provides more information than 1D NMR by plotting data in a space defined by two frequency axes. There are several types of 2D NMR experiments including COSY, NOESY, and HETCOR. COSY identifies spin-coupled protons by showing cross peaks between protons that are directly bonded. NOESY correlates protons that are near each other in space but not necessarily directly bonded. HETCOR plots 1H and 13C spectra on separate axes and connects carbon signals to bonded proton signals. 2D NMR techniques provide additional structural information about molecules compared to traditional 1D NMR.