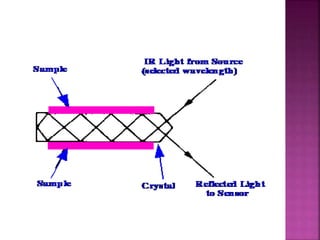
Attenuated total reflectance (ATR) spectroscopy allows samples to be examined directly in the solid or liquid state without preparation by passing infrared radiation through an infrared-transmitting crystal with a high refractive index. The infrared beam undergoes total internal reflection within the crystal and evanescent waves penetrate into the sample in contact with the crystal, producing its infrared spectrum. ATR is useful for analyzing liquids, solids, powders, and other samples with little preparation and can be applied in fields like pharmaceuticals, chemicals, forensics, and biomedical research.