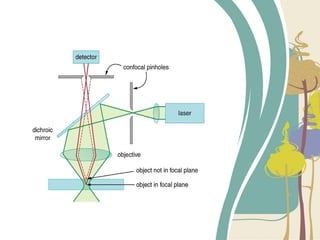
Confocal microscopy is a noninvasive imaging technique that enables high-resolution analysis of ocular surface microstructure. It was invented in 1957 and works by illuminating samples point-by-point and rejecting out-of-focus light to generate optical sections. There are various types including tandem scanning, scanning slit, and laser scanning confocal microscopes. Clinical applications include imaging corneal layers, assessing wound healing after refractive surgery, and diagnosing infections. It allows evaluation of conditions like diabetic keratopathy by quantifying changes in subbasal nerve fibers. Advanced techniques like second harmonic generation further study corneal collagen architecture.








![Laser scanning confocal microscopy
The HRT III with Rostock Corneal Module (HRT-RCM).
has 63× lens and optional 10 × to see deeper (lens,zonules)
uses 670 nm diode laser and provides 1micron resolution.
HRT-RCM does applanate cornea and the use of PMMA
disposabel cap and gel is mandatory for the exam.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cornealconfocalmicroscopy-190802084008/85/Corneal-confocal-microscopy-10-320.jpg)