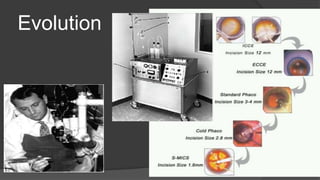
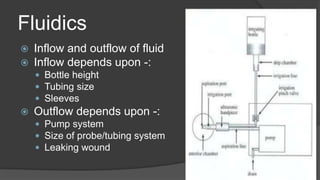
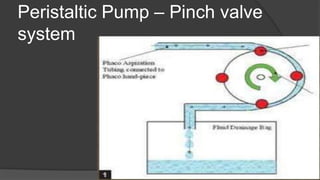
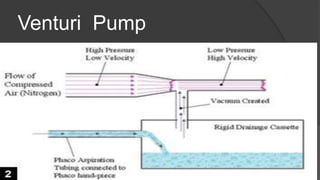
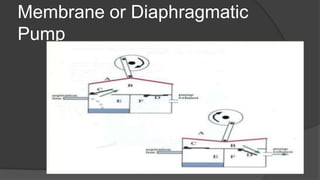
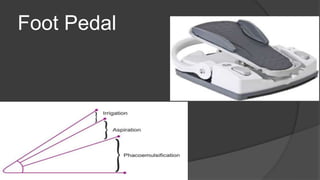
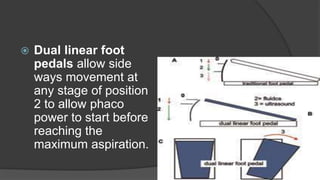
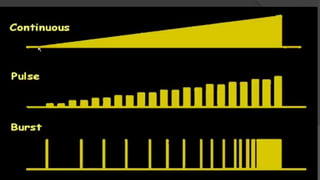
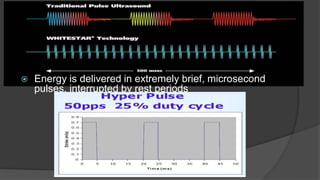
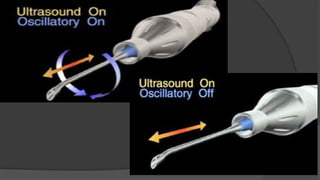
The document discusses advancements in phacoemulsification techniques, presented by Dr. Paresh Nichlani and moderated by Prof. K.N. Jha, aimed at improving cataract surgery outcomes. Key highlights include innovations in ultrasound energy delivery, fluidics management, and new technologies such as the Aqualase device and femtosecond laser-assisted surgery. The focus is on minimizing complications, enhancing visual acuity, and improving efficiency through better power modulation and foot pedal systems.