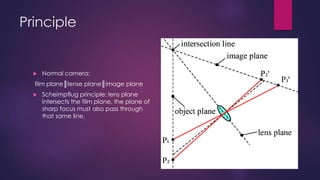
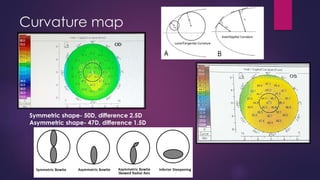
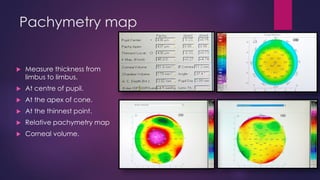
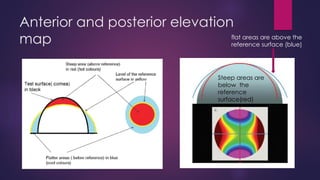
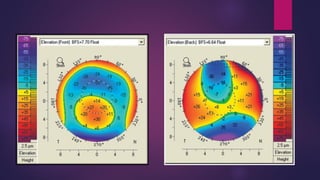
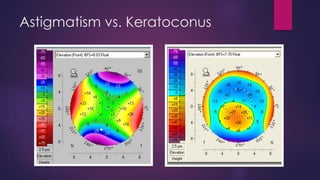
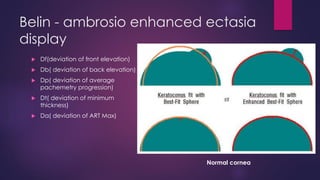
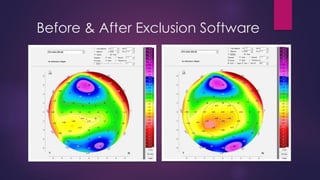
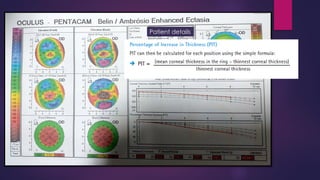
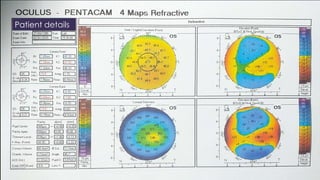
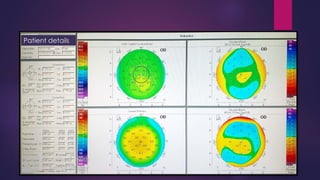
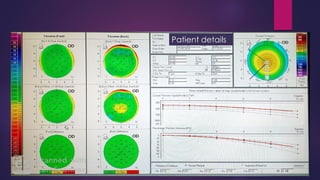
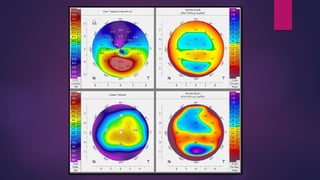
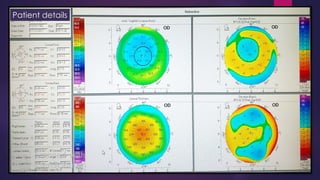
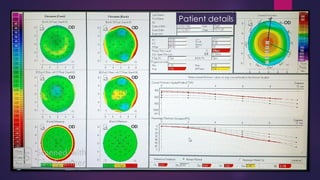
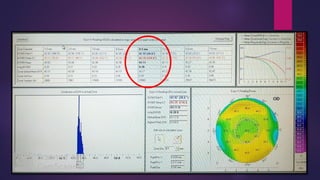
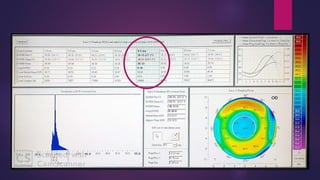
The document discusses Pentacam, a diagnostic tool that uses a rotating Scheimpflug camera to capture 50 images in 2 seconds and create a 3D model of the anterior eye segment. It has applications in assessing corneal ectasia, refractive surgery, corrected intraocular pressure, corneal aberrations, IOL power calculation, and densitometry. The Pentacam provides curvature, pachymetry, and elevation maps. It can detect ectasia by identifying if the highest curvature, thinnest thickness, and steepest elevation points coincide. The Pentacam is also used to measure corneal aberrations via Zernike analysis and calculate accurate IOL power for patients with previous refractive surgery or cataracts.