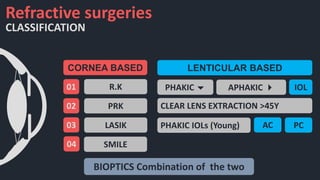
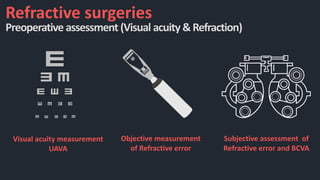
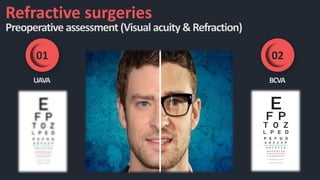
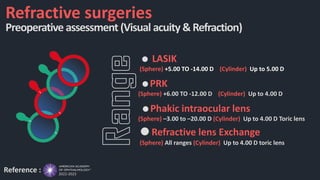
This document discusses the various techniques used in refractive surgeries to correct vision, including steps for evaluating patients and determining suitability. It describes the history and evolution of refractive surgeries. The main techniques covered are corneal-based procedures like LASIK, PRK, and SMILE as well as lenticular procedures using phakic intraocular lenses. For LASIK specifically, it outlines the surgical technique and potential complications. Contraindications for refractive surgeries are also stated.