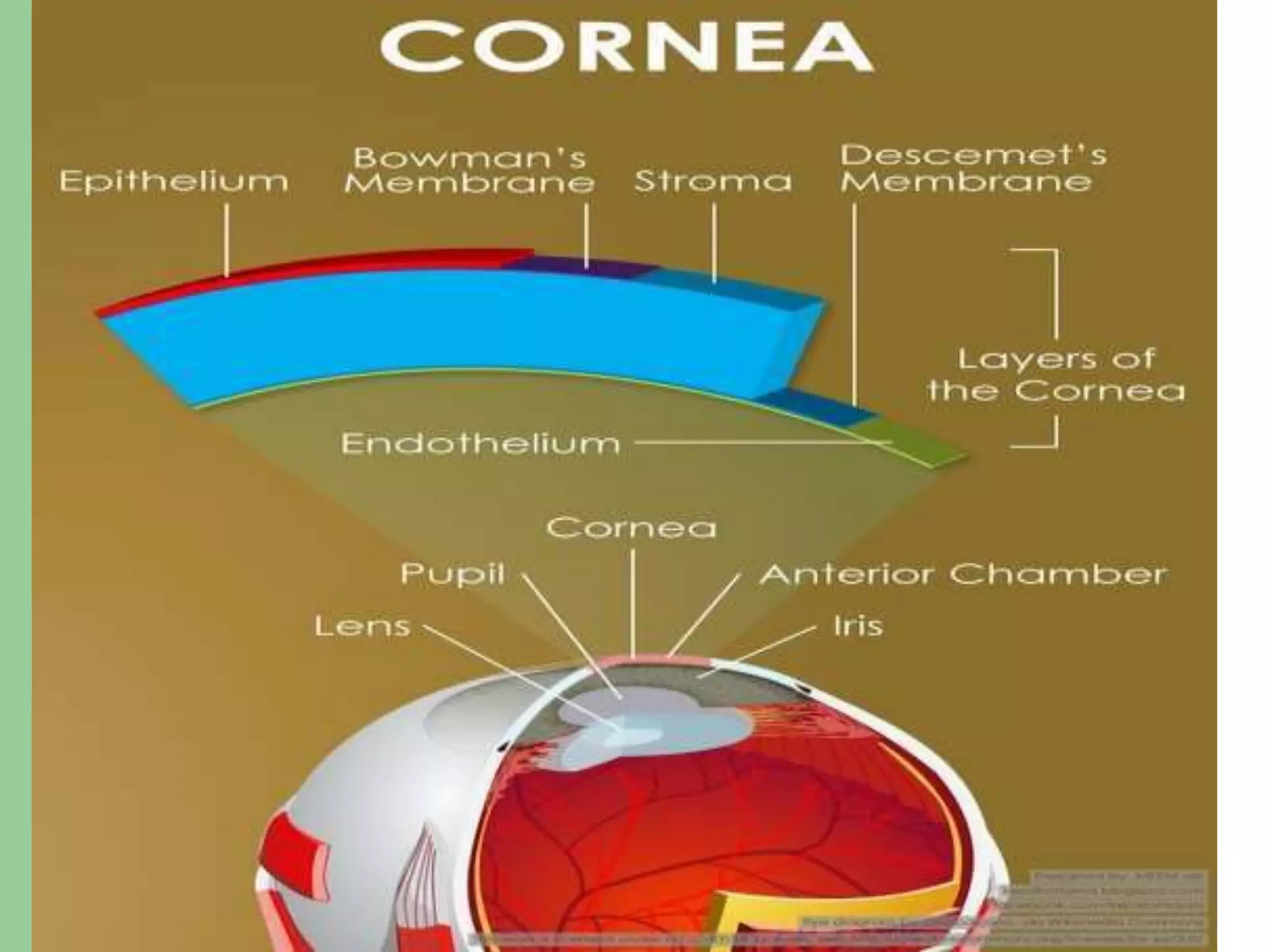
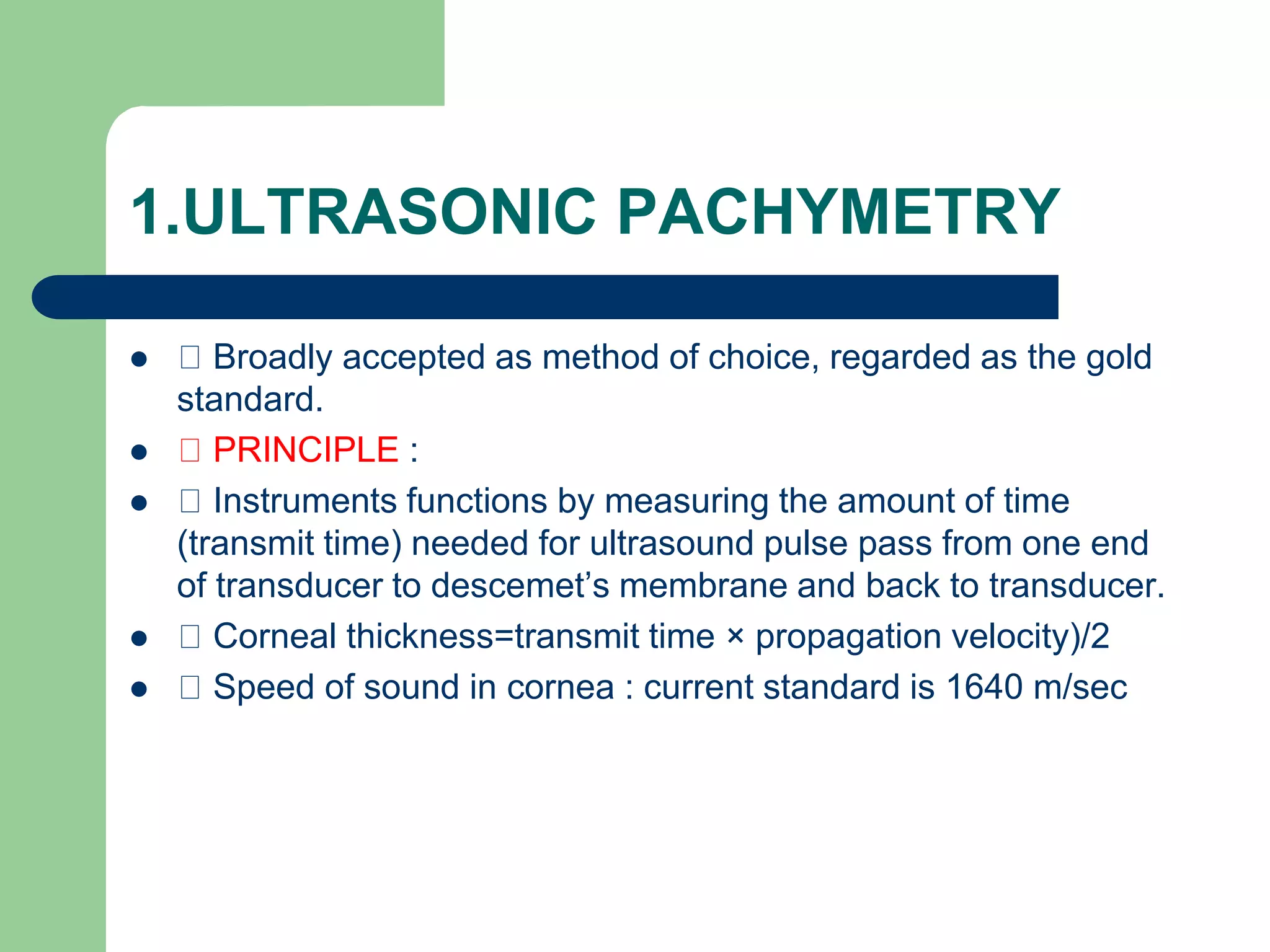
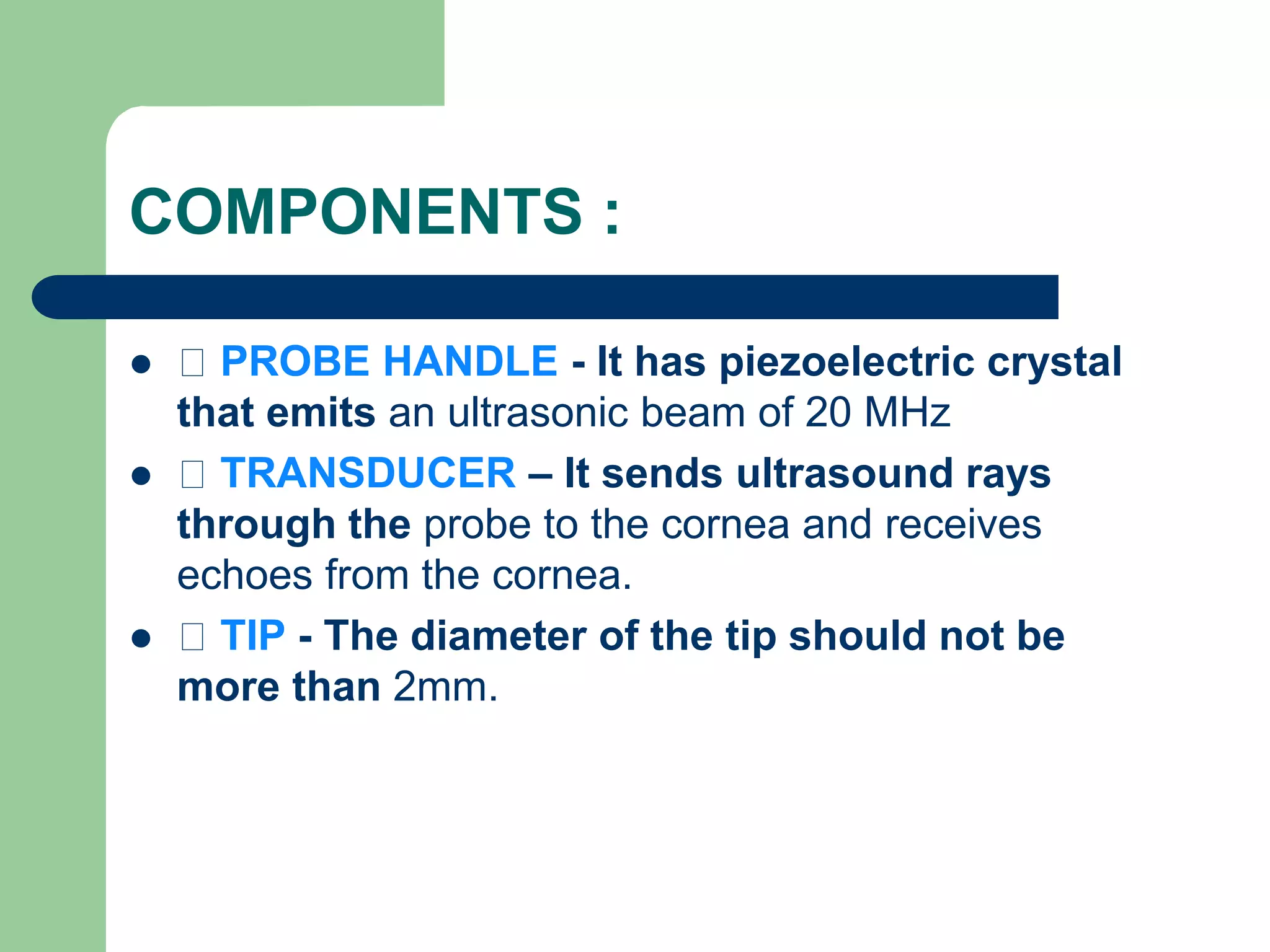
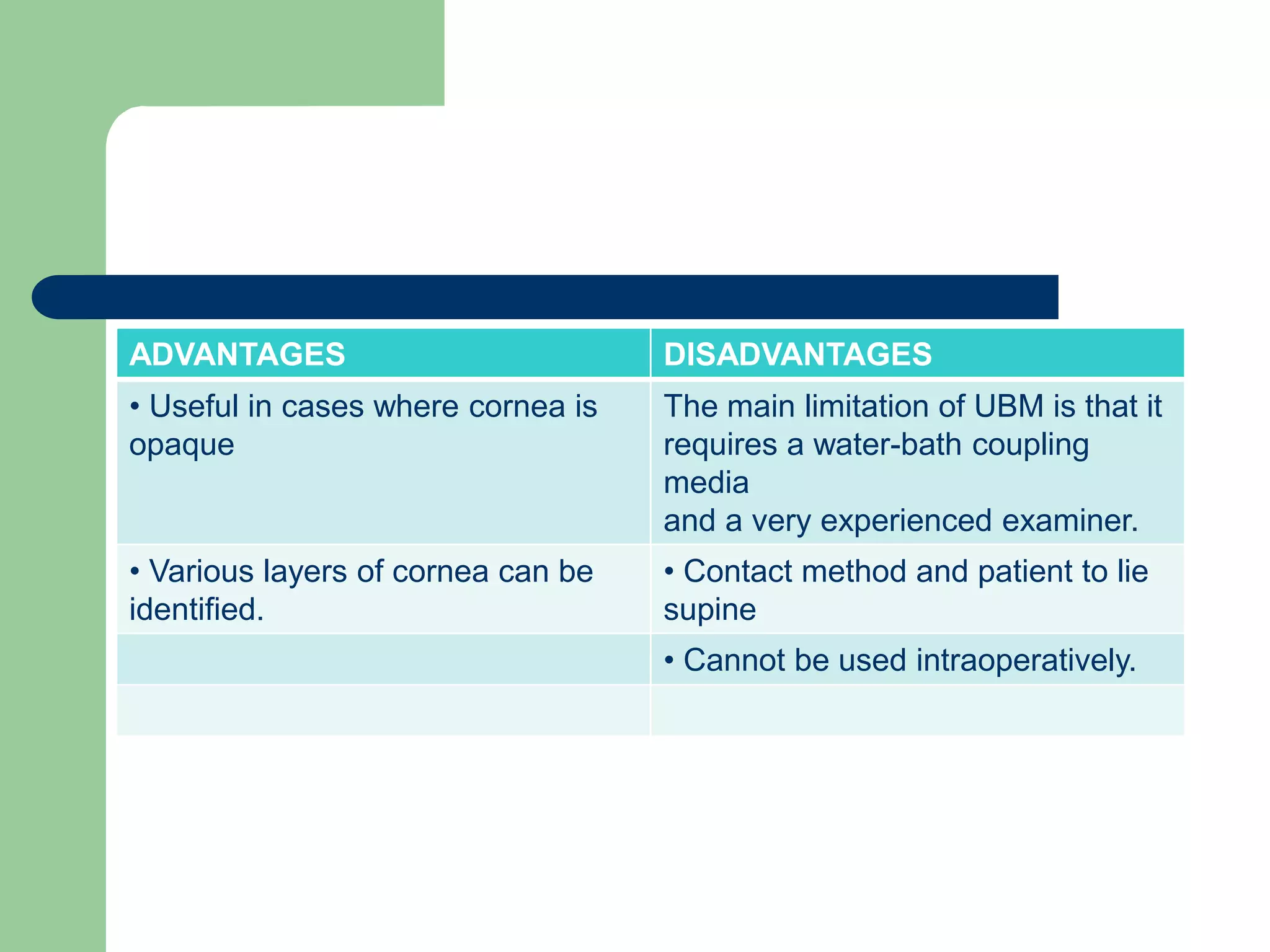
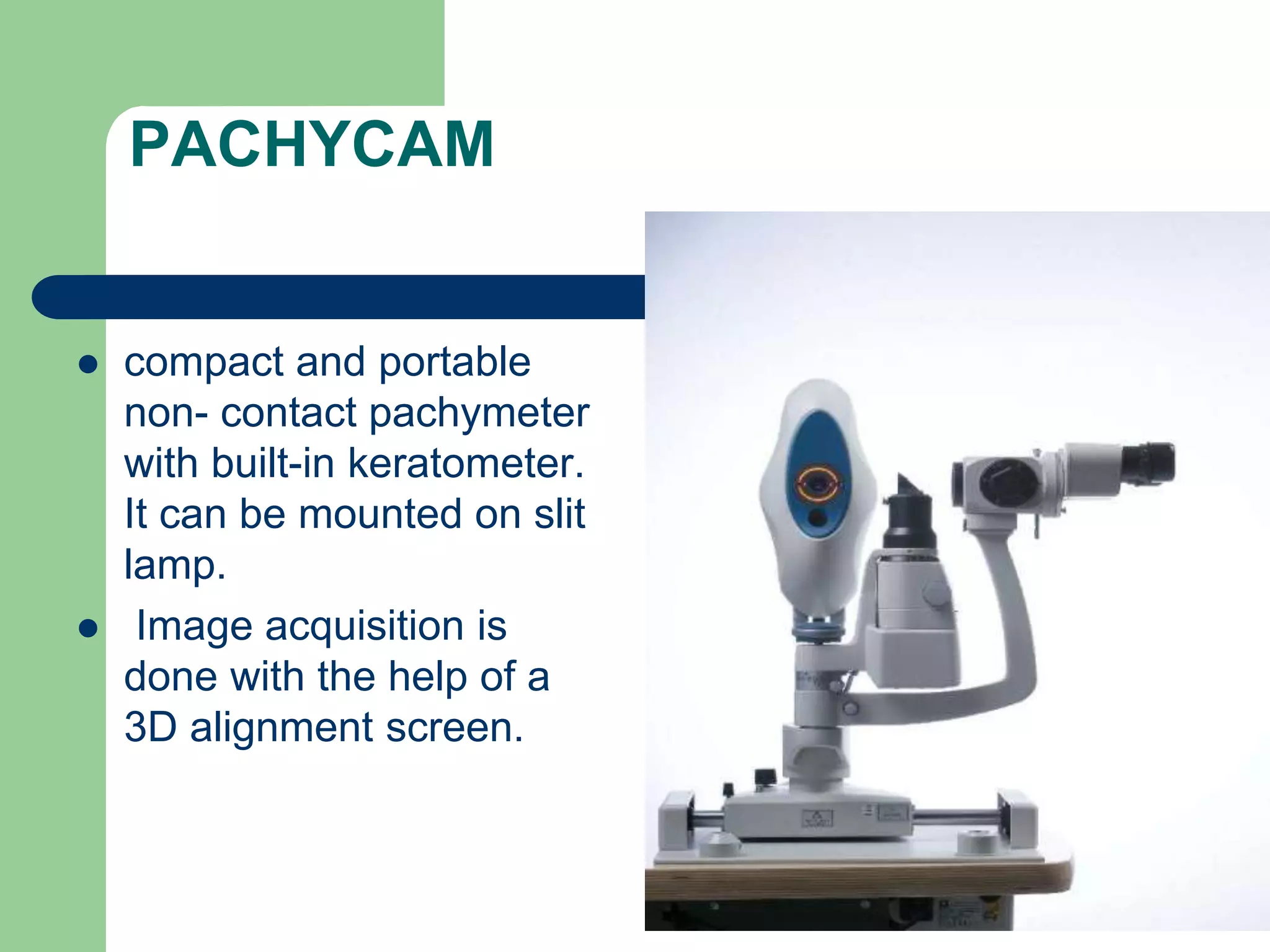
Corneal pachymetry is the measurement of corneal thickness, which is an important indicator of corneal health. Various techniques for measuring corneal thickness are described, including ultrasonic pachymetry (considered the gold standard), ultrasound biomicroscopy, manual and specular optical pachymetry, anterior segment optical coherence tomography, Pentacam, and Pachycam. Factors like ethnicity and refraction can affect normal corneal thickness measurements. Measurements outside the normal range of 500-575 microns may indicate conditions like corneal thinning, edema, or abnormal intraocular pressure.