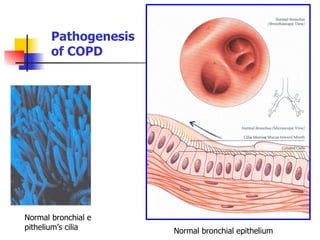
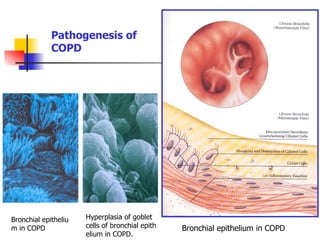
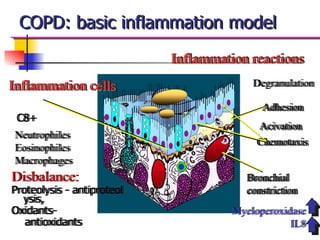
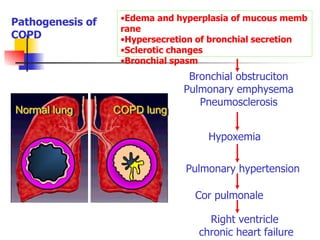
This document discusses chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It defines COPD as a progressive lung disease characterized by airway obstruction due to chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The major risk factor is tobacco smoke. Symptoms include cough, sputum production and shortness of breath. Diagnosis involves lung function tests showing irreversible airway obstruction. Treatment focuses on smoking cessation, bronchodilators, antibiotics for exacerbations, oxygen therapy, and pulmonary rehabilitation.