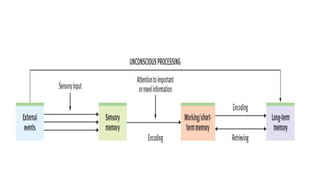
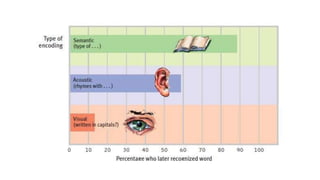
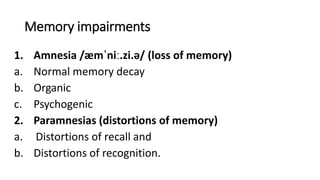
The document discusses three types of memory: sensory memory, which briefly registers sensory input; short-term memory, which retains information for about 20 minutes; and long-term memory, responsible for encoding and storing information. It explores various memory impairments, including amnesia, paramnesias, and specific phenomena like confabulation and false memories, while distinguishing between organic and psychogenic causes of memory disorders. The document further elaborates on different types of amnesia, their mechanisms, and related phenomena like déjà vu.