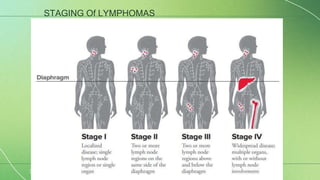
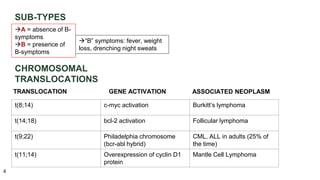
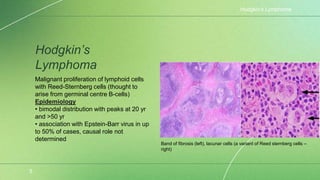
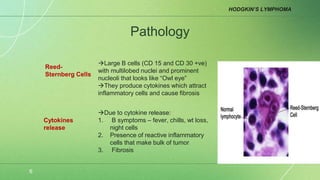
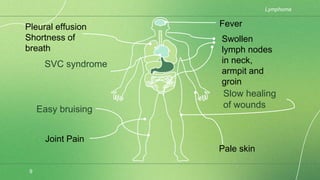
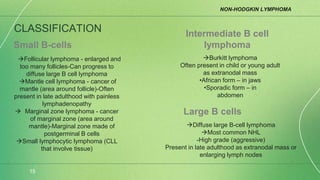
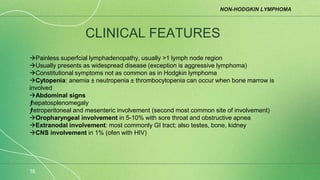
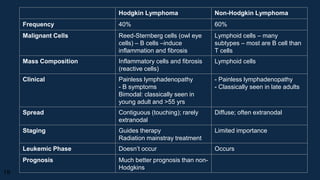
Lymphoma is a collection of lymphoid malignancies in which malignant lymphocytes accumulate at lymph nodes and lymphoid tissues, leading to lymphadenopathy, extranodal disease, and constitutional symptoms. There are two main types: Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells and causes inflammation and fibrosis. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma encompasses a variety of subtypes of B-cell and T-cell lymphomas that present with widespread disease. Staging guides treatment for Hodgkin's lymphoma while it is less important for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.