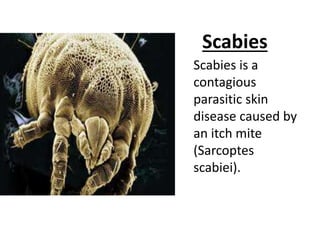
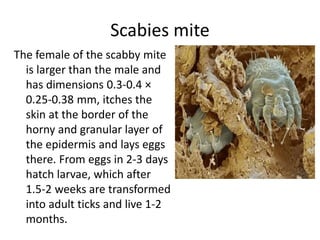
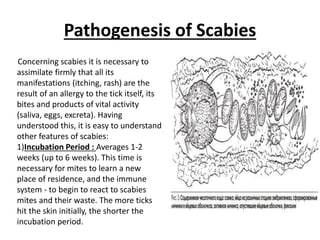
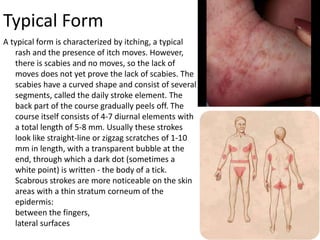
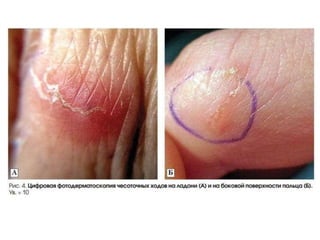
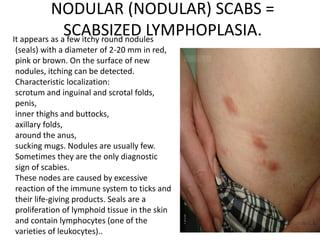
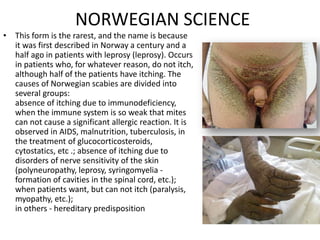
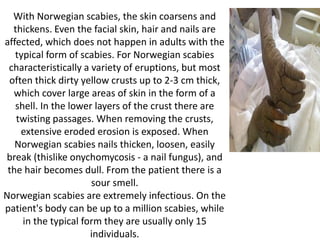
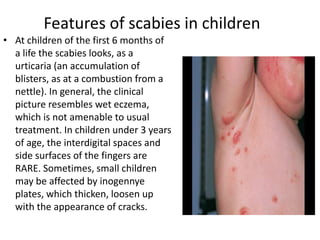
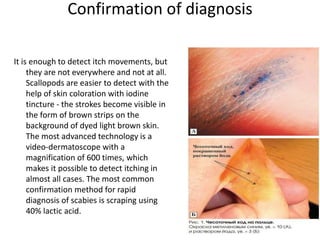
Scabies is a contagious skin disease caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which leads to severe itching and allergic skin reactions due to its bites and waste. The disease spreads primarily through direct skin contact and can manifest in various forms, including typical and Norwegian scabies, with symptoms differing between children and adults. Treatment involves using specific medications and ensuring that all individuals in close contact undergo preventive measures to eliminate the infestation.