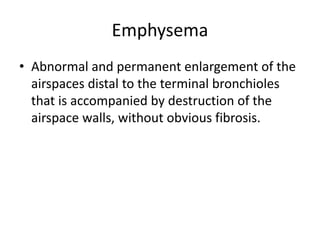
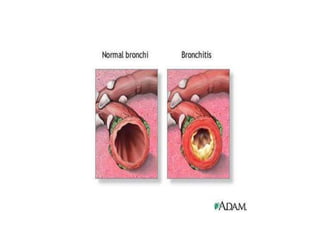
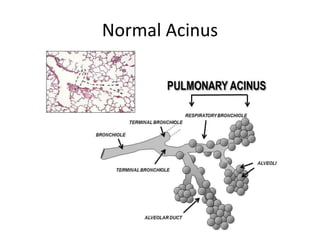
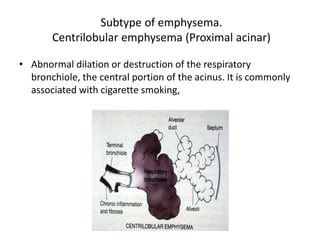
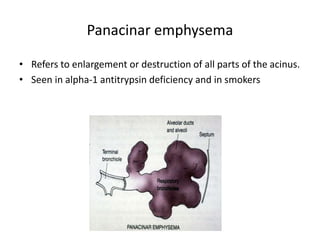
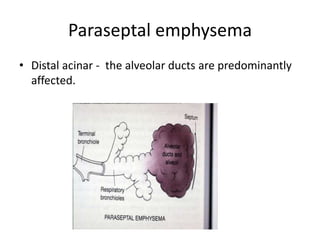
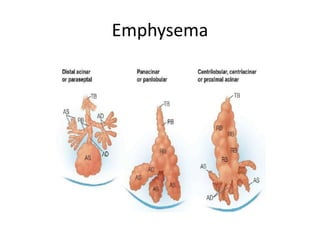
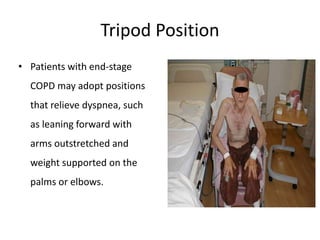
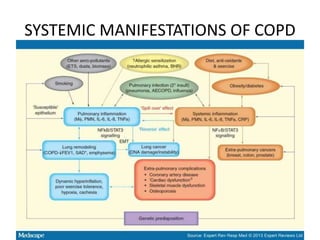
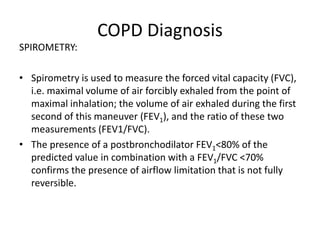
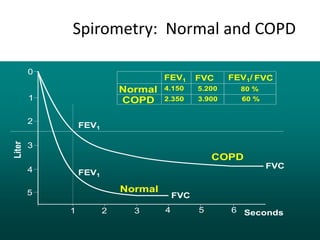
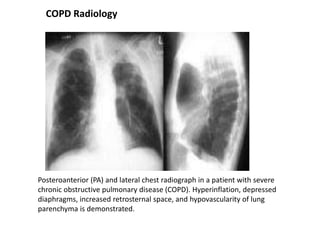
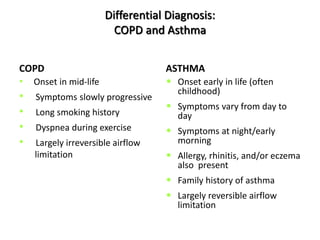
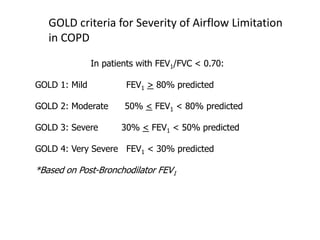
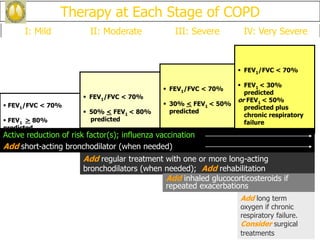
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by persistent airflow limitation that is usually progressive. It includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. COPD is diagnosed based on spirometry showing airflow limitation. Symptoms include breathlessness, cough, and wheezing. Management involves reducing risk factors, managing stable COPD with bronchodilators and rehabilitation, and treating exacerbations with bronchodilators and glucocorticoids. The severity of COPD is classified based on lung function, and treatment is escalated based on severity from short-acting bronchodilators to long-term oxygen for very severe COPD.