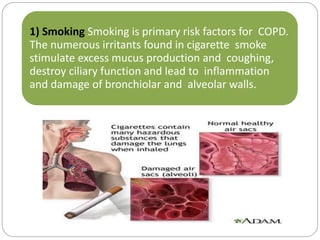
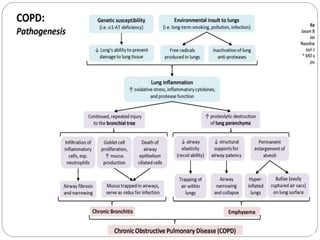
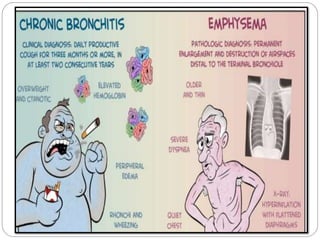
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) refers to two commonly co-existing lung diseases: chronic bronchitis and emphysema. In COPD, less air flows in and out of the airways due to narrowing of the airways. The primary risk factor for COPD is smoking, as the irritants in cigarette smoke damage the lungs over time. Other risk factors include air pollution, occupational exposures, infections, and genetic conditions like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. The main clinical features of COPD are chronic cough, sputum production, wheezing, chest tightness, dyspnea on exertion, weight loss, and respiratory insufficiency.