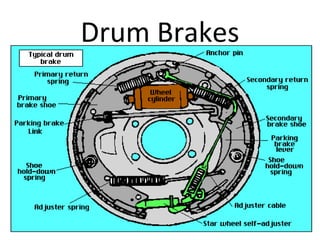
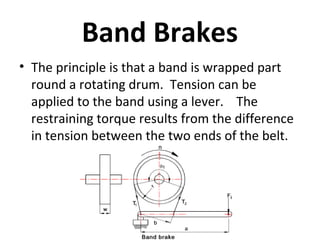
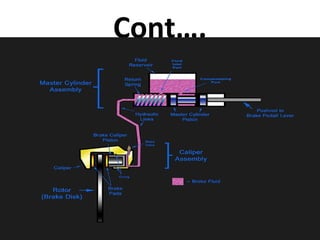
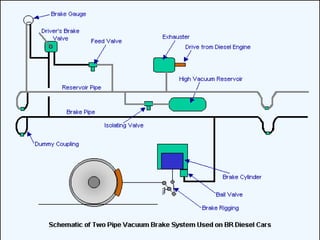
This document summarizes different types of braking systems used in vehicles. It describes the basic requirements and components of braking systems. The main types discussed are drum brakes, disc brakes, and various power brakes such as hydraulic, vacuum, air, and electric brakes. It provides details on the construction and operation of these different braking methods. The purpose is to classify and explain the functioning of common braking technologies used to stop vehicle motion.