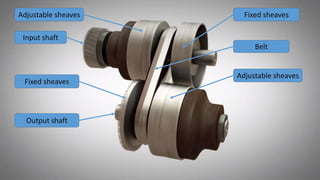
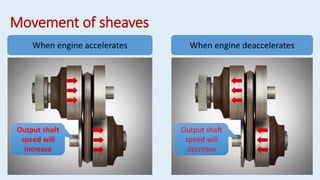
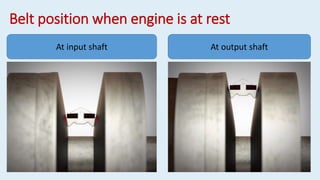
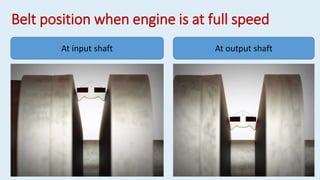
This document discusses continuously variable transmissions (CVTs). It describes the key parts of a CVT including a belt, fixed sheaves, adjustable sheaves, and centrifugal weights. It explains how a CVT works by varying the diameter of the input and output sheaves to provide an infinite range of gear ratios. CVTs allow the engine to run at optimal speeds for efficiency. Some advantages are smooth gear changes, compact design, and cost effectiveness. CVTs are used in many passenger vehicles and motorcycles.