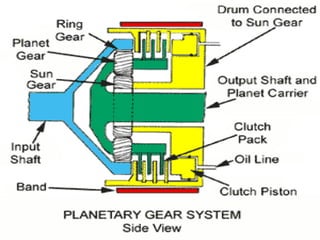
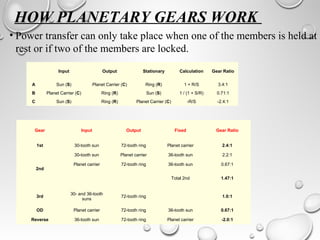
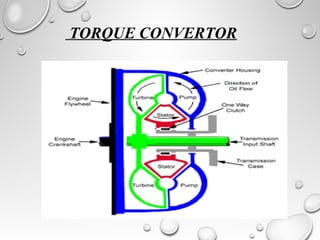
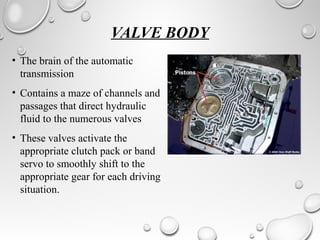
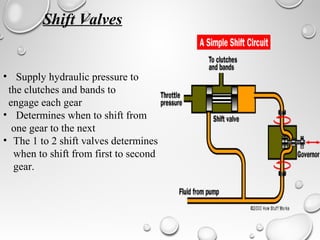
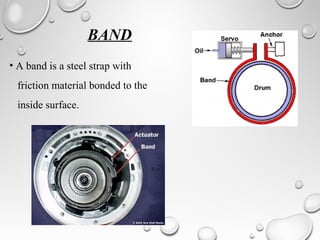
The document discusses automatic transmissions for automobiles. It begins by introducing automatic transmissions and their main components. There are two main types: ones using planetary gears and continuously variable transmissions. It focuses on transmissions using planetary gears. These systems use a planetary gear set, torque converter, hydraulic system, governor and computer controls to automatically shift gears based on driving conditions. The hydraulic system sends fluid through the transmission to control shifting, while the governor and computer monitor vehicle speed and other factors to determine appropriate shift points.