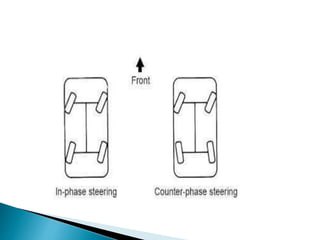
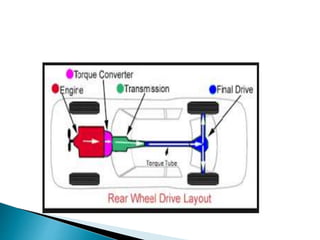
This document discusses four wheel steering (4WS) systems. It begins by defining 4WS as a rear wheel steering system that improves stability at high speeds. It then explains the basic components and types of steering systems, including front wheel, rear wheel, and 4WS. The document outlines the different modes in a 4WS system, including mechanical, hydraulic, and electro/hydraulic. It describes how 4WS provides benefits like improved handling, reduced driver fatigue, and increased stability at both high and low speeds. Finally, it states that a successful 4WS system could allow for development of a highly maneuverable vehicle with stability and obstacle climbing capabilities.