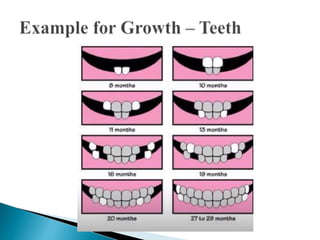
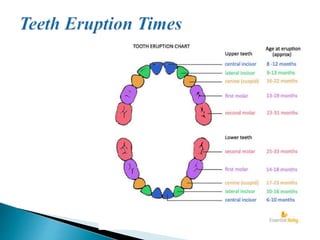
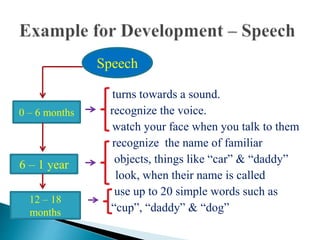
Growth refers to increases in physical size, height, and weight, and is a quantitative and additive process. It is influenced by hereditary and environmental factors and stops at a particular point in life. Development, on the other hand, refers to qualitative changes that improve functional ability and occur across the lifespan through maturation and experience. Key differences between growth and development include that growth involves body changes while development involves orderly changes in character, and growth measures can be accurate while development involves subjective interpretation. Both nature and nurture influence human development, with nature determining genetic traits and nurture involving environmental experiences.