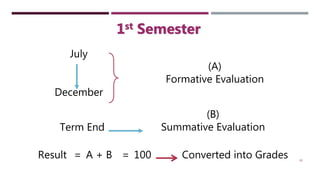
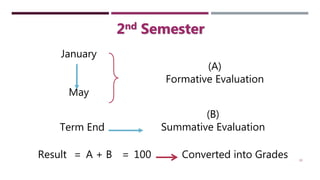
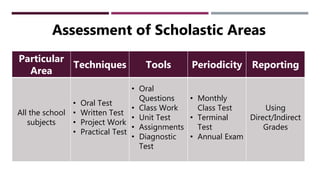
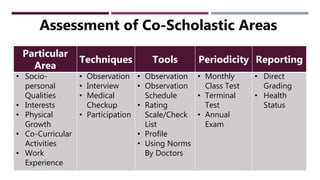
The document discusses Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE) in the educational context, emphasizing its role in ongoing assessment of student development across scholastic and co-scholastic areas. It outlines objectives, historical background, and the significance of formative and summative evaluations, highlighting benefits and challenges in implementing CCE in schools. The document concludes with suggested solutions for effective CCE execution, including proper teacher training and infrastructure improvements.